Investing in Stocks: A Beginner’s Guide October 21, 2021

What this report is about:
- Understand what a Stock is
- Difference between Common and Preference Stocks
- Where and how to purchase
Back in March 2020, the investing world got into a frenzy during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic, retail and institution investors hurried to purchase shares on the cheap.
As one without any prior knowledge in investing, you were probably fearful and chose to stand on the side-lines.
But these questions remain:
How do I start Investing?
How do I tell if a stock is worth investing?
Most importantly, how do I take the first step?
In this article, we will discuss and guide you as you journey into the world of investing.
What is a stock?
A stock is a security that represents a partial ownership of a company. This allows the owner of the stock to a proportion of the company’s assets and profits equivalent to the amount of stocks they own.
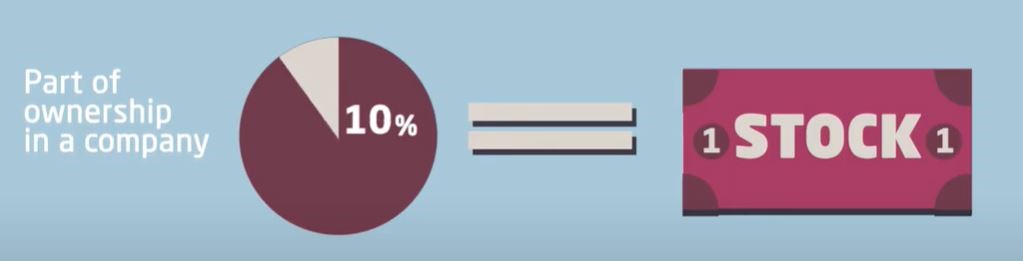 Source: Capital.com
Source: Capital.com
Understanding stocks
Generally, listed companies will issue shares to the public on stock exchanges to raise funds for their operations. When someone buys a stock of a particular company, that person is a shareholder of the company. This means that the shareholder is now a partial owner of the issuing company.
Ownership is determined by the numbers of shares a person has in comparison to the total number of outstanding shares. For example, if a person owns 20 shares of the company, and the total outstanding shares of the company is 100 shares, that person owns and have claim to 20% of the company’s assets and earnings.
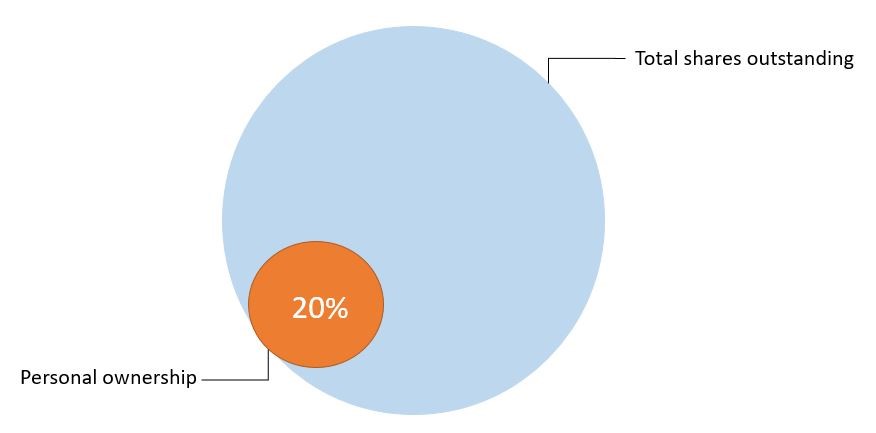
Shareholders do not actually own the company, rather they own shares issued by the corporations. This means that if a company goes bankrupt, its shareholders’ personal assets are not at risk even if the judge orders to sell all of the company’s assets. Similarly, if a major shareholder goes bankrupt, the person cannot sell the company’s asset to pay off their debt.
Evaluating a stock
There are many metrics that investors use when evaluating a stock. However for most, they will look at the company’s prospectus as it is a legal document where the company provides full details with respect to the investment offerings. A prospectus will have basic information such as:
• Summary of the company’s background and financial information
• The name of the company issuing the stock
Another way to check if a stock is worth investing is to read their annual/quarterly reports, which can be found on the company’s website under Investor Relations section. An annual report will give investors a rough gauge on the company’s financial soundness, management confidence and sources of revenue which are important criteria for evaluating a company.
In addition to the information available, brokerage firms and banks will also share their views of a particular stock via research reports. This will provide a holistic view to the particular stocks which investors are considering.
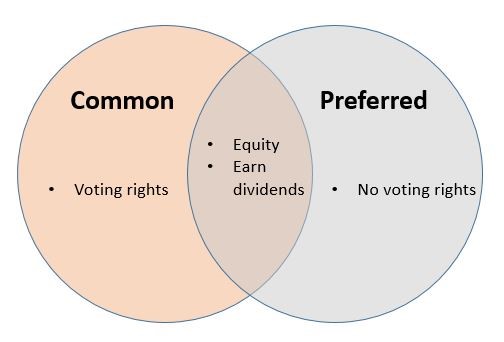
Common vs preferred stock
Investors of common stocks have voting rights in the company while investors with preferred stocks are not allowed to vote in shareholder meetings. However, preferred stock holders will receive dividends before common stock holders.
Differences between Stocks and Bonds
Bonds are issued by companies to raise capital as well. Bond holders are creditors to the company, and are entitled to interest payment based on their principal value. The interest payment however, is typically fixed unlike dividends. Creditors have priority over stockholders in the event of bankruptcy when a company is forced to sell its assets to repay the debt.

Listing of companies
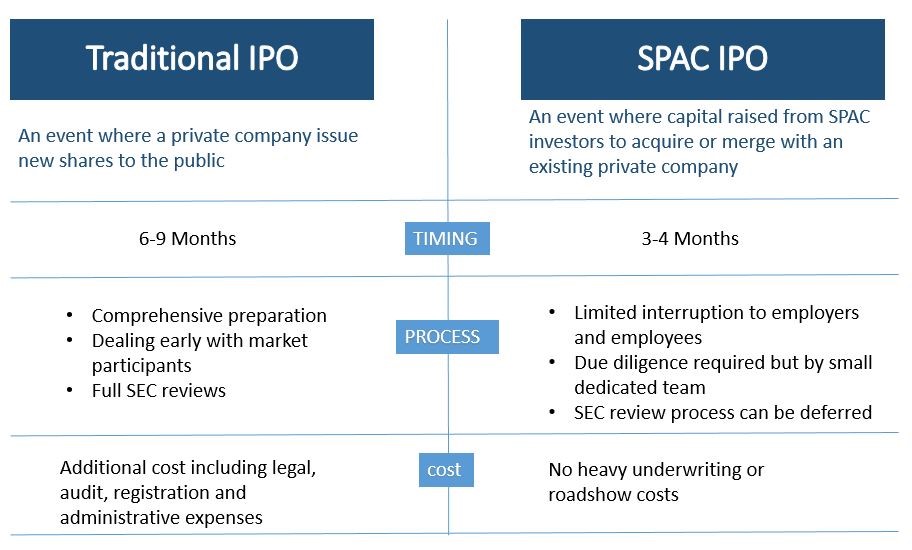
Companies are required to be listed if they want their shares to be traded publicly through an Initial Public Offering (IPO). The traditional ways of IPOs such as fixed price offering and book building offering are different from IPO through Special Purpose Acquisition Company (SPAC).
Below is a comparison table between a traditional IPO and a SPAC IPO.
How and where do you buy stocks?
Stocks are traded on stock exchanges. After a company goes public, their shares will be allowed to trade on the exchange they are listed in. Investors are required to open a brokerage account in order to purchase stocks on the exchange. For example, a POEMS trading account allows investors to buy stocks across 26 Exchanges at a competitive price.
 Source: POEMS platform
Source: POEMS platform
Delisting of companies
Delisting is the removal of a company from a stock exchange. Companies can voluntarily delist, but are usually delisted because of actions such as ceased operations, bankruptcy or not meet listing requirements.
Companies who fail to meet listing requirements such as maintaining a minimum share price, financial ratios and sales level will be issued warnings. To avoid being delisted, they may undergo a reverse split of their shares.
Exchange Fees and Corporate Actions
When trading with any brokerage firm, investors have to take note of fees involved in trading. Other than the commission fees that most investors are aware of, there are other fees which are often overlooked. Such fees include custody fee, platform fee, maintenance fee, inactivity fee and deposit or withdrawal fees.
In addition, for Singapore stocks, Clearing fee, SGX trading fee and Goods and services Tax (GST) are included in your trading fees as well.
Investors are also subjected to corporate actions of the company they invested in. Corporate actions is the term used to describe changes to a company’s structure. As mentioned previously, a reverse split of share to prevent delisting may be utilised. A reverse split is a corporate action. Actions of the company will be further explained and elaborated in our next article on Corporate Actions.
In Summary
After understanding some of the basics of stock investing, it could be rewarding if the right stocks are being picked. However, before investing, it is important to do due diligence and have an understanding of the underlying risks that come with stock investing when compared to other asset classes such as bonds.
Sources
Adam Hayes. (2021). How does the stock market work?
https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/082614/how-stock-market-works.asp
What is shares trading and why is it important to traders?
https://capital.com/trade-stocks.
Why trade stocks with POEMS?
https://www.poems.com.sg/products/stocks/
Disclaimer
These commentaries are intended for general circulation. It does not have regard to the specific investment objectives, financial situation and particular needs of any person who may receive this document. Accordingly, no warranty whatsoever is given and no liability whatsoever is accepted for any loss arising whether directly or indirectly as a result of any person acting based on this information. Opinions expressed in these commentaries are subject to change without notice. Investments are subject to investment risks including the possible loss of the principal amount invested. The value of the units and the income from them may fall as well as rise. Past performance figures as well as any projection or forecast used in these commentaries are not necessarily indicative of future or likely performance. Phillip Securities Pte Ltd (PSPL), its directors, connected persons or employees may from time to time have an interest in the financial instruments mentioned in these commentaries. Investors may wish to seek advice from a financial adviser before investing. In the event that investors choose not to seek advice from a financial adviser, they should consider whether the investment is suitable for them.
The information contained in these commentaries has been obtained from public sources which PSPL has no reason to believe are unreliable and any analysis, forecasts, projections, expectations and opinions (collectively the “Research”) contained in these commentaries are based on such information and are expressions of belief only. PSPL has not verified this information and no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made that such information or Research is accurate, complete or verified or should be relied upon as such. Any such information or Research contained in these commentaries are subject to change, and PSPL shall not have any responsibility to maintain the information or Research made available or to supply any corrections, updates or releases in connection therewith. In no event will PSPL be liable for any special, indirect, incidental or consequential damages which may be incurred from the use of the information or Research made available, even if it has been advised of the possibility of such damages. The companies and their employees mentioned in these commentaries cannot be held liable for any errors, inaccuracies and/or omissions howsoever caused. Any opinion or advice herein is made on a general basis and is subject to change without notice. The information provided in these commentaries may contain optimistic statements regarding future events or future financial performance of countries, markets or companies. You must make your own financial assessment of the relevance, accuracy and adequacy of the information provided in these commentaries.
Views and any strategies described in these commentaries may not be suitable for all investors. Opinions expressed herein may differ from the opinions expressed by other units of PSPL or its connected persons and associates. Any reference to or discussion of investment products or commodities in these commentaries is purely for illustrative purposes only and must not be construed as a recommendation, an offer or solicitation for the subscription, purchase or sale of the investment products or commodities mentioned.
About the author
Li Wei Wei
Equities Specialist Toa Payoh Phillip Investor Center
Wei Wei graduated from University of Exeter with a Bachelor’s Degree in Economics and Finance. He specializes in US equities and has worked in a family office to horn his skills in fundamental analysis. He believes in long term investment and the importance of stay invested throughout every business cycles.

 Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap  How to soar higher with Positive Carry!
How to soar higher with Positive Carry! ![[Smart Park] Buy Insurance, Get Rich Quick? Not Exactly, But This Comes Close [Smart Park] Buy Insurance, Get Rich Quick? Not Exactly, But This Comes Close](https://www.poems.com.sg/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Valerie-Lim-LI-X-SMART-Park-Article-300x157.jpg) [Smart Park] Buy Insurance, Get Rich Quick? Not Exactly, But This Comes Close
[Smart Park] Buy Insurance, Get Rich Quick? Not Exactly, But This Comes Close  Deciphering the Updates: Understanding the latest CPF Changes
Deciphering the Updates: Understanding the latest CPF Changes 









