How to Use Advanced Order Types to Invest: Part I April 13, 2021

At a glance:
- Advanced Order Types are risk-management tools that help investors and traders enter or exit the market according to their specified prices and quantities
- Advantages of using them include improved execution speed and minimised losses. Disadvantages include order execution is not guaranteed and the chance of you paying higher prices
- Know your trading objectives in order to choose the right Advanced Order Types
Reading time: 10 minutes
Risk is always prevalent in trading and managing it is a trader’s biggest challenge.
When markets are uncertain, a simple yet powerful way of trading with precision is to use Advanced Order Types. These allow you to programme your orders such as applying stops and limits for all your trades and monitor market movements effectively.
What is Advanced Order Type?
Advanced Order Types are a risk-management tool that can help investors and traders enter or exit the market according to the price and quantity specified. There are many order types in the market, each designed for a purpose.
Traders use different order types to deal with market fluctuations. When paired with technical analysis, Advanced Order Types can help them make smarter and more informed decisions.
Why should you use order types?
Order types can help you:
- Trade with precision
- Improve execution speed
- Minimise risks and losses when markets turn unfavourable
- Opportunistically get into positions when market conditions are favourable
POEMS offers up to 11 order types across its platforms:
| Order Type | |||
| Limit Order | |||
| Stop Limit Order*Only for NASDAQ, NYSE, AMEX, SGX | |||
| Limit-If-Touched (LIT)*Only for SGX**Only for NASDAQ, NYSE, AMEX, SGX | |||
| If-Done Order | |||
| One-Cancels-The-Other (OCO)*Only for SGX | |||
| Market Order*Only for NASDAQ, NYSE, AMEX | |||
| Market-On-Open (MOO)*Only for NASDAQ, NYSE, AMEX | |||
| Market-On-Close (MOC)*Only for NASDAQ, NYSE, AMEX | |||
| Good-Till-Date (GTD)*Only for SGX**Only for NASDAQ, NYSE, AMEX, HKSE, BURSA, SGX | |||
| Fill-Or-Kill (FOK)*Only for SGX | |||
| Immediate-Or-Cancel (IOC)*Only for SGX |
How to use Advanced Order Types to invest
All order types have their pros and cons. To use Advanced Order Types, it is crucial to know how they work and when best to apply them.
1. Limit Order vs. Market Order
Limit Orders and Market Orders are the most basic order types for every investor.
What is Limit Order?
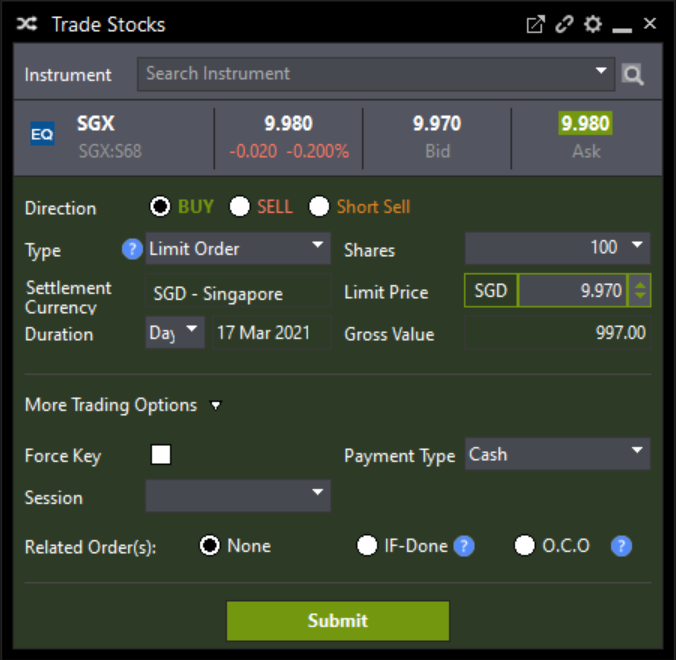
For example, if you submit a Buy Limit Order at S$9.97, your order will only be filled when the stock price is equal to or less than S$9.97.
Pro: This order type gives you control over how much you pay, as you set the minimum or maximum price to buy or sell a particular counter.
Con: This order type does not guarantee order execution. This can be a drawback during market volatility, when you may miss out on opportunities.
What is Market Order?
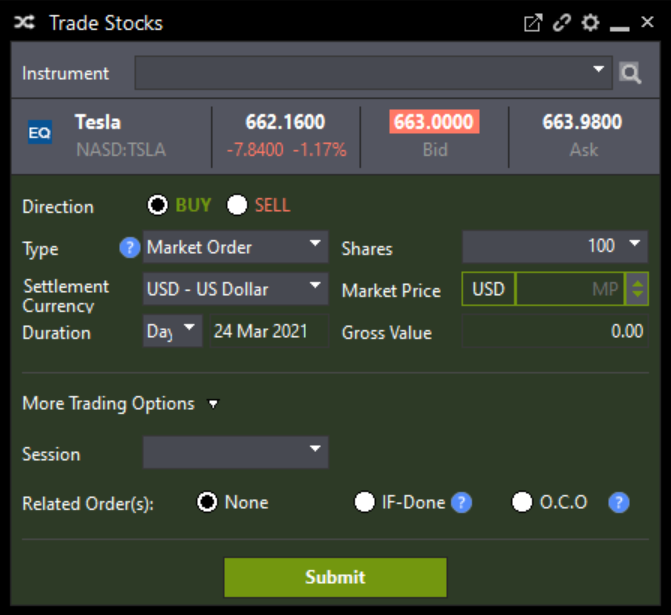
Unlike Limit Orders which fill orders based on price, Market Orders do not look at price. Instead, they are executed at the current market price. The last traded price may not be the price at which your Market Order would be executed. In Market Orders, share prices are secondary to the speed of executing a trade.
Pro: This order type guarantees an order’s immediate execution.
Con: Care should be taken when submitting such an order type during fast-moving market conditions. This is because your executed price can deviate from the last traded price.
When to use Limit Order and Market Order?
Market Orders are meant to be executed immediately at current market prices. They are used when investors want to trade a stock without delay.
Limit Orders allow you to set the minimum or maximum price at which you are willing to sell or buy a stock. They are used when you only want to buy or sell at a certain price.
For example, if you are only willing to pay S$6.20 for an ABC share, you could submit a Limit Order. However, if you are comfortable with the current traded price and just want to buy or sell shares in ABC, you would choose a Market Order.
For more information on Limit Orders and Market Orders, click here.
2. Fill-or-Kill (FOK) Order vs. Immediate-or-Cancel (IOC) Order
Currently only available for SGX stocks on POEMS Pro, traders can leverage FOK and IOC to trade large quantities of shares.
What is FOK?
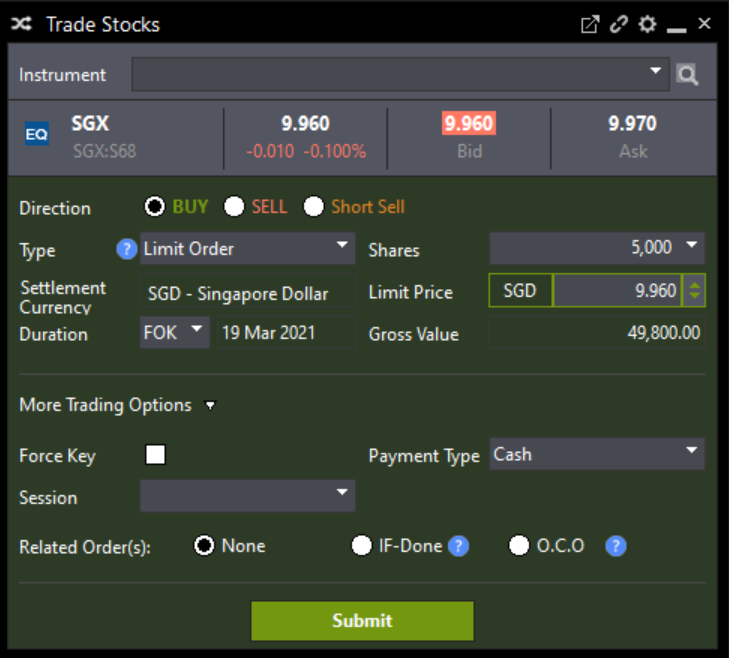
The order will only be fulfilled when it satisfies three conditions:
- There is enough supply to meet the quantity you specify
- The order price is the same as the market price
- The order can be executed immediately
Let’s say the current price of SGX is S$9.96. You submit a FOK order at S$9.96 to purchase 5,000 SGX shares. If the market price rises to S$9.97, your order cannot be filled immediately and will be cancelled.
What is IOC?
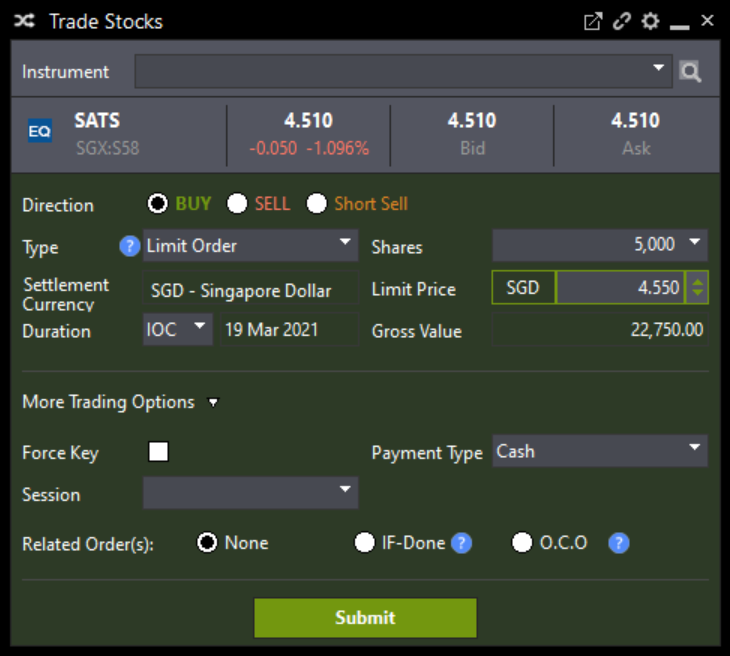
An IOC order can be useful if traders do not need to fill their entire orders but rather want to capitalise on a certain price point. IOC allows investors to make a quick purchase or sale of some of the shares, if not all.
For example, a trader places an IOC order to buy 5,000 SATS shares at S$4.55 each. In the market’s current order book, there are 2,000 shares with an asking price of S$4.55. The order would immediately fill 2,000 shares at S$4.55 and cancel the unfilled portion of 3,000 shares.
When to use FOK and IOC?
FOK and IOC are typically used for large orders. Their main difference is that IOC allows for partial filling of orders. FOK does not.
Generally, FOK is used by active traders for purchasing large quantities of shares at a specific price and time. If you do not want to trade beyond a particular price and want to fill your order in its entirety, you need to choose FOK.
IOC is typically used by traders for large orders to be executed at one price and not various price levels. They are prepared that their order may not be filled in their entirety. This order type is useful for traders who want to buy shares that are immediately available at a preferred price.
3. Market-On-Open (MOO) vs. Market-On-Close (MOC)
Trading in the US market? Here are two useful order types you can apply.
What is MOO?
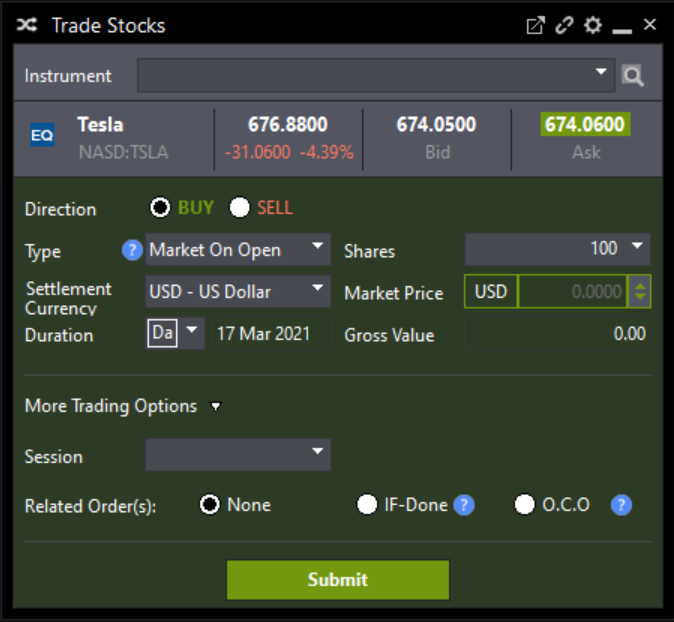
Assume that the media has reported that the market is expecting ABC Company to post positive quarterly earnings. Believing that the shares of ABC Company will rise the next trading day, a trader places a MOO order to buy ABC shares before the market opens. Be careful of leveraging MOO for such purposes. If ABC’s quarterly earnings fall short of expectations, its stock price may decline.
What is MOC?
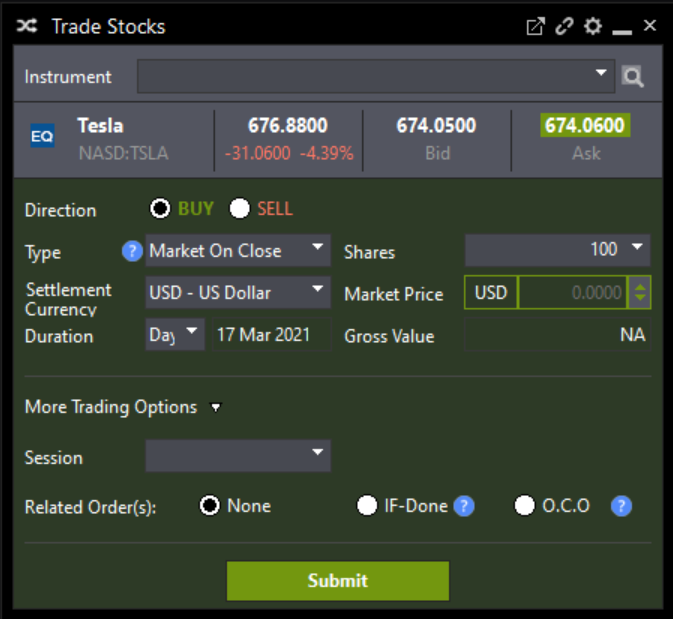
Generally, this order type is used when a trader expects the price of a stock to move drastically over a short period of time, typically overnight. Some traders also use this order type to secure a stock price at or close to the end of the trading day in anticipation of bigger moves and sharp reversals. It is only available on US exchanges.
For example, XYZ Company is expected to report negative earnings after the market closes. In anticipation that the stock price will fall, a trader may place a MOC order to sell XYZ shares at the end of the trading day to curtail his losses in the event of a massive overnight sell-off.
When placing a MOC order, traders should note that there is risk of end-of-day price fluctuations.
When to use MOO and MOC?
MOO is placed before the market opens while MOC is placed during the market’s trading session. MOO is filled at the day’s opening price while MOC is executed at the day’s closing price.
Traders use MOO orders for convenience, particularly those who want to trade at the day’s opening price but are unable to monitor the market when it opens.
MOO orders are also used when traders anticipate a good buying or selling opportunity when the market opens. For example, a trader may expect a company’s stock price to rise or fall significantly in anticipation of positive or negative news on the company after the market closed the previous day.
On the other hand, traders use MOC orders when they expect share prices to move significantly over a short period of time, typically overnight. This can occur when traders anticipate news that could affect the company positively or negatively. Placing a MOC order ensures that the traders execute their orders before the stock moves on the next trading day.
For more information on MOO and MOC, click here.
Advanced Order Types are available on POEMS Mobile 2.0, POEMS 2.0 and POEMS Pro. Trade with precision today and leverage market movements effectively with a host of Advanced Order Types!
| Stay tuned as we will be back with Part 2 of Advanced Order Types! |
POEMS suite of trading platforms is made to suit the needs of all traders and investors. Open a Cash Plus Account to enjoy commission fee as low as 0.08%, no minimum* when you trade equities. Jumpstart your investing journey with POEMS now! *T&Cs Apply.
You may also be interested in…
Disclaimer
These commentaries are intended for general circulation. It does not have regard to the specific investment objectives, financial situation and particular needs of any person who may receive this document. Accordingly, no warranty whatsoever is given and no liability whatsoever is accepted for any loss arising whether directly or indirectly as a result of any person acting based on this information. Opinions expressed in these commentaries are subject to change without notice. Investments are subject to investment risks including the possible loss of the principal amount invested. The value of the units and the income from them may fall as well as rise. Past performance figures as well as any projection or forecast used in these commentaries are not necessarily indicative of future or likely performance. Phillip Securities Pte Ltd (PSPL), its directors, connected persons or employees may from time to time have an interest in the financial instruments mentioned in these commentaries. Investors may wish to seek advice from a financial adviser before investing. In the event that investors choose not to seek advice from a financial adviser, they should consider whether the investment is suitable for them.
The information contained in these commentaries has been obtained from public sources which PSPL has no reason to believe are unreliable and any analysis, forecasts, projections, expectations and opinions (collectively the “Research”) contained in these commentaries are based on such information and are expressions of belief only. PSPL has not verified this information and no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made that such information or Research is accurate, complete or verified or should be relied upon as such. Any such information or Research contained in these commentaries are subject to change, and PSPL shall not have any responsibility to maintain the information or Research made available or to supply any corrections, updates or releases in connection therewith. In no event will PSPL be liable for any special, indirect, incidental or consequential damages which may be incurred from the use of the information or Research made available, even if it has been advised of the possibility of such damages. The companies and their employees mentioned in these commentaries cannot be held liable for any errors, inaccuracies and/or omissions howsoever caused. Any opinion or advice herein is made on a general basis and is subject to change without notice. The information provided in these commentaries may contain optimistic statements regarding future events or future financial performance of countries, markets or companies. You must make your own financial assessment of the relevance, accuracy and adequacy of the information provided in these commentaries.
Views and any strategies described in these commentaries may not be suitable for all investors. Opinions expressed herein may differ from the opinions expressed by other units of PSPL or its connected persons and associates. Any reference to or discussion of investment products or commodities in these commentaries is purely for illustrative purposes only and must not be construed as a recommendation, an offer or solicitation for the subscription, purchase or sale of the investment products or commodities mentioned.



 Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024  From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation  How to soar higher with Positive Carry!
How to soar higher with Positive Carry!  Why 2024 Offers A Small Window of Opportunity and How to Position Yourself to Capture It
Why 2024 Offers A Small Window of Opportunity and How to Position Yourself to Capture It