Introduction to ETFs August 20, 2020

Introduction
You’ve probably heard of Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) from the investment community. It’s usually the same description – they are low cost and efficient diversification financial products.
But the ETF world is much more complicated than that. It is filled with many different types of ETFs and technical jargons that may confuse or even intimidate the everyday investors.
Fret not, in this article, we will take you through the basics of ETFs, the terminologies in an ETF factsheet and the things to look out for before investing in ETFs.
This article will guide you to learn how to utilise ETFs for your investment journey.
What is an ETF?
ETFs are open-ended investment funds with a primary objective of tracking its benchmark index.
It is a marketable security that trades like a common stock on stock exchanges around the world. As an investment fund, ETF holds a diversified portfolio of securities to achieve its index replication objective.
In summary, ETFs are investment funds listed on exchanges and trade on exchanges like a stock.
Types of ETFs
Market Capitalisation Weighted ETFs
These ETFs track their respective capitalisation-weighted indexes. The index components are selected and weighted according to the total market value of their outstanding share units (share price * total number of outstanding share units).
For example, the Straits Times Index (STI) comprises the top 30 companies listed on the Singapore Exchange (SGX). If the market capitalisation of one of the STI’s constituents falls below the top 30 ranking, another better performing company will replace it on the index.
Examples of Market Capitalisation Weighted ETFs
| Index | ETF |
| S&P 500 Index |
|
| Straits Times Index |
|
| FTSE China A50 Index |
|
| Hang Seng Index |
|
Smart Beta ETFs
Unlike traditional Market Capitalisation Weighted ETFs, Smart Beta ETFs use an alternative rules-based index construction strategy.
By adopting a rule-based approach to selecting its constituents, Smart Beta ETF aims to quantify its index criteria and eliminate any irrational behavioural factors from portfolio management.
ETF issuers often launch Smart Beta ETFs to target any gap in the saturated ETF market space and serve unmet investors’ needs.
Examples of Smart Beta ETFs include Lion-Phillip S-REITs ETF (SGX: CLR) and Phillip Sing Income ETF (SGX: OVQ).
Actively Managed ETFs
Actively managed ETFs belong to a class of ETF that does not adhere to the passive index replication strategy. They invest in a portfolio of securities that are subjectively chosen by their fund managers.
The fund managers have the liberty to adjust the securities and portfolio allocation within the fund while not being limited to the fixed rule of tracking an index.
Actively managed ETFs have the potential to outperform their benchmark indexes through the investment decisions made by their fund managers. However, the higher transaction cost of managing the funds may result in higher expense ratios when compared with traditional index-tracking ETFs.
Nikko Asset Management launched the first actively managed ETF in Asia on HKEx in June 2020. The NikkoAM Active E-Games ETF (HKEx: 9091) has the flexibility to rebalance its underlying assets daily to adapt to the ever-changing landscape of the E-Games industry.
Leveraged and Inverse ETFs
There are special classes of ETFs available in the market that allow investors to leverage or short their investments directly without the need to deposit a margin or borrow stocks respectively.
The availability of leveraged and inverse ETFs allows investors to hedge their portfolios or engage in tactical trading to gain exposure to specific market trends.
Leveraged and inverse ETFs are highly volatile trading instruments meant for short-term trading purposes only.
ETF Replication Method
The following are ways for an ETF to achieve its index-tracking objective:
1) Full Physical Replication
Full Physical Replication ETFs invest all of its assets in the constituents of the benchmark index, in proportion to the weight of the constituents in the index.
2) Sampling/Partial Replication
Instead of investing all of its assets in the constituents of the benchmark index, an ETF may choose to invest in only some of the constituents in the benchmark index. There are various reasons for adopting the sampling replication technique:
- To improve the performance of the ETFs by omitting underperforming securities
- It is impossible or not cost-effective to purchase all the securities in the benchmark index
3) Synthetic Replication
Synthetic ETFs purchase futures, options and other derivatives instruments in exchange for the benchmark index performance. There are various reasons for adopting this synthetic replication approach:
- To gain access to obscure or less liquid markets
- To reduce tracking error
- To replicate unique benchmark index
- To overcome the problem of incurring high transaction costs (e.g. Commodity ETFs do not have to incur storage, insurance and logistics costs)
ETF Factsheet Terminologies
An ETF factsheet contains several technical terms and definitions. Moreover, different ETF issuers present their ETFs’ factsheet data differently, which may further confuse investors.
Nevertheless, once an investor learns the different terminologies used in an ETF factsheet, he/she will be able to make informed decisions about his/her choices of ETFs in the future.
Below are the common terminologies used in an ETF factsheet:
| Terminology | Definition |
| Expense Ratio | An ETF fund issuer will incur management, administrative, legal, auditing and custodian fees, as well as transaction costs etc in the operations of the ETF. Expense ratio is the total annual fee that ETF charges their shareholders for managing the ETF.Investors do not have to make any additional payments to the fund managers as expense ratio is deducted from the Net Asset Value (NAV) of the ETF. |
| Number of Holdings | The number of holdings is the number of different financial assets held under the ETF.For example, STI ETF will have the top 30 companies stocks listed on the SGX under its holdings. |
| Asset Under Management (AUM) / Total Net Assets | The total market value of all the financial assets held under the ETFs. |
| Shares Outstanding | The total number of ETF units that is circulating and held by investors/participants in the markets. |
| Net Asset Value (NAV) | The actual value per unit of an ETF. The NAV of the ETF is not the market price of the ETF. |
| Premium / Discount | The percentage price difference of the ETF that is trading above or below the NAV. |
Benefits of ETFs
To date, ETFs are getting immensely popular among investors and the number of ETFs available in stock exchanges globally has grown from only one ETF in 1993 to almost 7,000 ETFs by the end of 2019.
So why are ETFs gaining popularity and what are the benefits of investing in ETFs? We shall explain them in detail in this section.
| Benefits | Description |
| Transparency |
|
| Diversification |
|
| Liquidity |
|
| Cost-effective |
|
| Variety |
|
Before I Trade ETFs
Investors who wish to trade ETFs should take note of the following:
With the exception of some SGX listed ETFs which are classified as Excluded Investment Products (EIP), all other SGX and overseas listed ETFs are classified as Specified Investment Products (SIP).
Investors will have to clear their Customer Account Review (CAR) in order to trade SIP.
You may visit SGX ETF Screener for more information on the classification of SGX listed ETFs.
For investors who wish to trade overseas listed financial products, they will have to acknowledge the Risk Warning Statement (RWS) with their respective brokers. In addition to the RWS, investors who wish to trade US listed financial products are required to submit their W-8BEN Form.
Figure 1: CAR, W-8BEN Form and RWS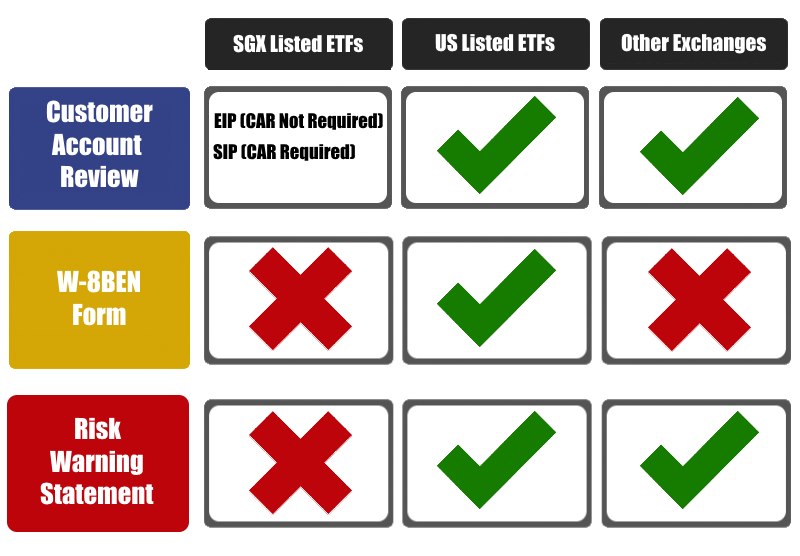
How Can I Trade ETFs
ETFs are traded like stocks on exchanges. You can trade SGX and overseas listed ETFs once you have opened a POEMS trading account and cleared the necessary requirements. There are over 3,300 ETFs available on our POEMS trading platform.
Investors can also consult their qualified financial advisors or investment professionals should they have any queries about ETFs.
Conclusion
ETFs have quickly grown in popularity because of their cost-effectiveness, transparency and liquidity. Moreover, ETFs offer the additional benefit of instant diversification.
The advent of ETFs allows investors to gain exposure to macro trends in a convenient and efficient manner. Investors need not choose specific individual stocks for their investment strategy. They can simply select the ETFs with the investment objectives that match their desired market theme or strategy.
With thousands of ETFs available in stock exchanges around the world, investors can now tailor-make their own portfolio to gain exposure to worldwide trends and asset classes.
Disclaimer
These commentaries are intended for general circulation. It does not have regard to the specific investment objectives, financial situation and particular needs of any person who may receive this document. Accordingly, no warranty whatsoever is given and no liability whatsoever is accepted for any loss arising whether directly or indirectly as a result of any person acting based on this information. Opinions expressed in these commentaries are subject to change without notice. Investments are subject to investment risks including the possible loss of the principal amount invested. The value of the units and the income from them may fall as well as rise. Past performance figures as well as any projection or forecast used in these commentaries are not necessarily indicative of future or likely performance. Phillip Securities Pte Ltd (PSPL), its directors, connected persons or employees may from time to time have an interest in the financial instruments mentioned in these commentaries. Investors may wish to seek advice from a financial adviser before investing. In the event that investors choose not to seek advice from a financial adviser, they should consider whether the investment is suitable for them.
The information contained in these commentaries has been obtained from public sources which PSPL has no reason to believe are unreliable and any analysis, forecasts, projections, expectations and opinions (collectively the “Research”) contained in these commentaries are based on such information and are expressions of belief only. PSPL has not verified this information and no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made that such information or Research is accurate, complete or verified or should be relied upon as such. Any such information or Research contained in these commentaries are subject to change, and PSPL shall not have any responsibility to maintain the information or Research made available or to supply any corrections, updates or releases in connection therewith. In no event will PSPL be liable for any special, indirect, incidental or consequential damages which may be incurred from the use of the information or Research made available, even if it has been advised of the possibility of such damages. The companies and their employees mentioned in these commentaries cannot be held liable for any errors, inaccuracies and/or omissions howsoever caused. Any opinion or advice herein is made on a general basis and is subject to change without notice. The information provided in these commentaries may contain optimistic statements regarding future events or future financial performance of countries, markets or companies. You must make your own financial assessment of the relevance, accuracy and adequacy of the information provided in these commentaries.
Views and any strategies described in these commentaries may not be suitable for all investors. Opinions expressed herein may differ from the opinions expressed by other units of PSPL or its connected persons and associates. Any reference to or discussion of investment products or commodities in these commentaries is purely for illustrative purposes only and must not be construed as a recommendation, an offer or solicitation for the subscription, purchase or sale of the investment products or commodities mentioned.
About the author
Joel Lim
ETF Specialist
Joel is the ETF Specialist from the ETF desk in Phillip Securities. He helps to provide sales support and trading ideas to retail investors, remisiers, in-house dealers, and fund managers. Joel also works closely with ETF issuers on new product and business development projects.

 All-in-One Guide to Investing in China via ETFs
All-in-One Guide to Investing in China via ETFs  Everything you need to know on Bitcoin ETFs
Everything you need to know on Bitcoin ETFs  Maximising your Tax Savings & Retirement Funds with SRS in Singapore
Maximising your Tax Savings & Retirement Funds with SRS in Singapore  Is There a “Fairest of Them All”?
Is There a “Fairest of Them All”?