Making an Impact with ESG ETFs September 20, 2019

Summary
- Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Investing has taken on increased significance in the investing world, with ESG incorporation asset under management accounting for one in four dollars of the total asset under professional management in the United States in 2018.
- There is an increasing number of research that shows a positive relationship between a company’s financial performance and its non-financial performance on ESG issues.
- As structural change occurs and investors become more socially conscious, ESG investing will continue to grow in popularity in the future.
- Investors can gain access to ESG investment strategies via ESG ETFs. Examples of ESG ETFs include SUSL, USSG, VSGX and ESGV.
Introduction
Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) investing is a term that is commonly associated with socially responsible investing, mission-related investing or sustainable investing. The term has previously been defined as investing that integrates ethical, personal or moral concerns into the investment process.
The origin of ESG investing dates as far back to a few centuries ago, whereby practitioners invest their money according to their personal religious beliefs. An increase in social activism has seen ESG investing rise to prominence over the years. From the boycotting of weapon-producing companies during the Vietnam War to the divestitures of operations away from the racist system of apartheid in South Africa, investors and corporations are often driven by their ethical, personal, religious or social values.1
Today, ESG investing has taken on increased significance and it is becoming an important focus for the investing world.
According to the US SIF’s Report on US Sustainable, Responsible and Impact Investing Trends, ESG incorporation asset under management accounted for US$12 trillion – or one in four dollars – of the US$46.6 trillion in total assets under professional management in the United States in 2018. This represents a 38 percent increase over 2016.2
The increase is mainly driven by clients’ demand for ESG incorporated funds or financial products and institutional investors’ needs to fulfil their mission agenda and to pursue social benefit.
What Does ESG Factors Stand For?
Environmental, Social and Governance, or ESG in short, are the three central factors in measuring the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment in a company or business. It involves evaluating how companies’ environmental, social and governance practices may affect the investment return potential.3
| ESG Factor | Description |
| Environmental | Includes companies that actively sought to reduce the negative effect on the environment by mitigating pollution, adopting alternative clean sources of energy and working towards sustainable business practices |
| Social | Includes companies that value human rights and diversity; value consumer protectionism; avoid vice industries; and/or advocate animal welfare |
| Governance | Includes companies that have rigourous corporate governance practices such as board independence, internal controls, auditing process and transparency in corporate disclosure |
The ESG factors are often incorporated into the investment process alongside traditional financial analysis. These factors help to better determine the future financial performance and sustainability of the companies.
For example, companies that value human rights and diversity through fair labour practices can gain access to a wider pool of talent, which in turn may benefit the companies’ financial performance in the long term.
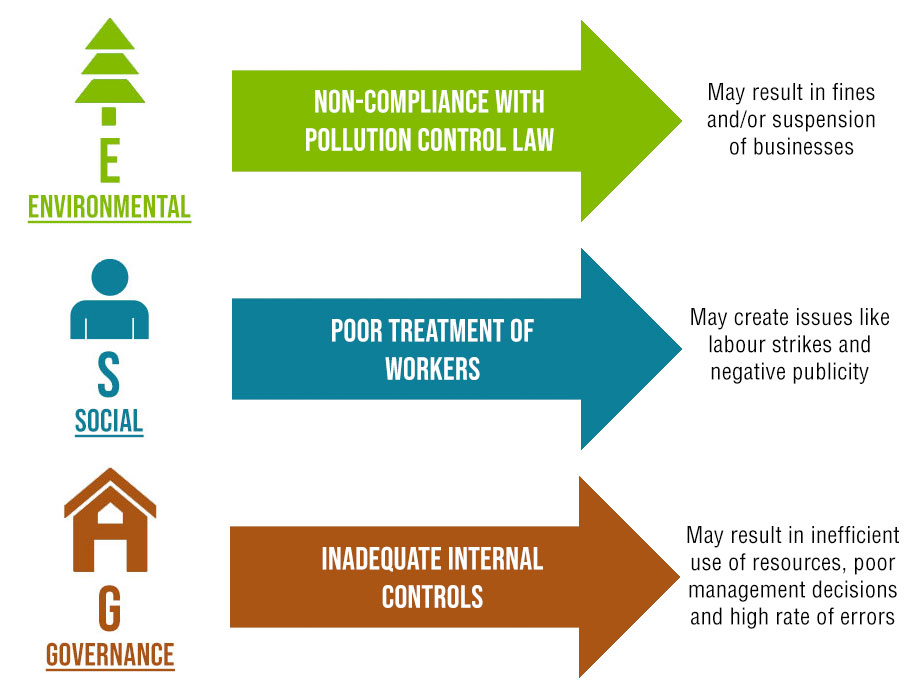
Furthermore, a failure to address the ESG factors can expose the companies to legal, regulatory, legislative, operational, financial and reputational risks.
Core Focus Area in ESG Investing or ESG Criteria
Figure 1: Examples of ESG Criteria Used by Investors
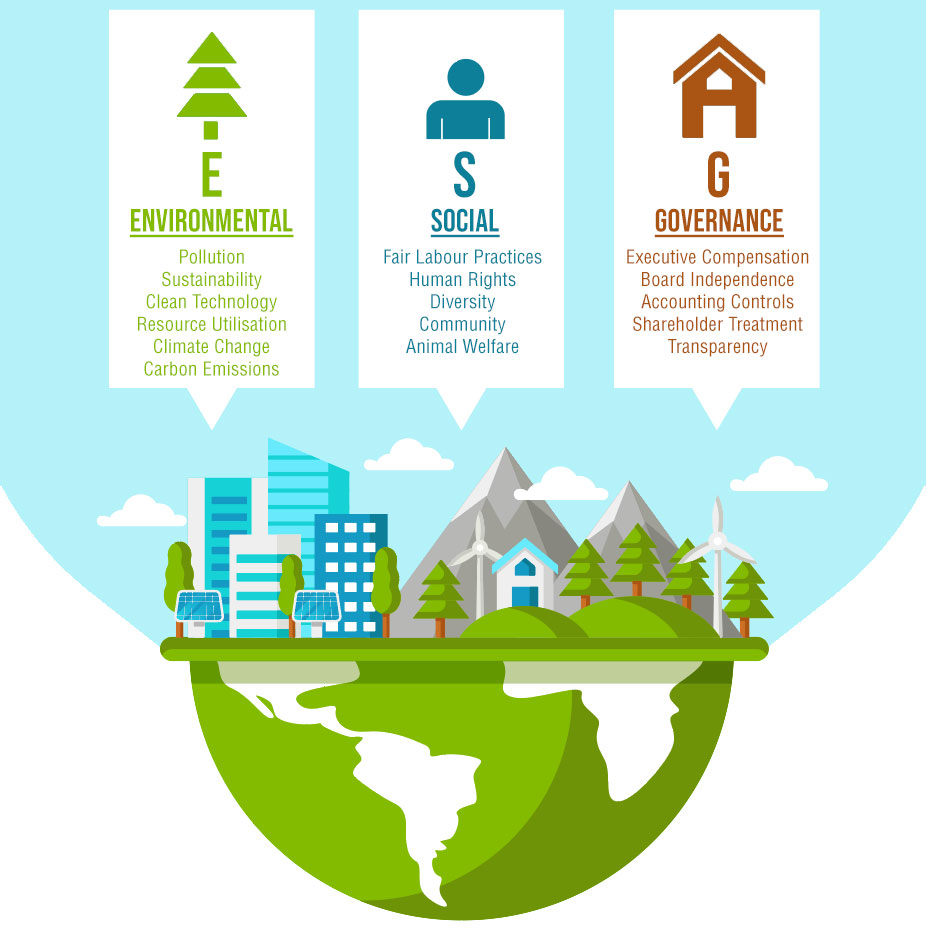
Figure 2: Analysis of How ESG Criteria may Affect Businesses
Three Common ESG Investors’ Objectives
Investors adopt ESG Investing for various reasons and investors’ objectives tend to converge around three main categories; Integration, Personal Values and Positive Impact.4
| Category | Objective | Description |
| Integration | Incorporating ESG factors to improve investment results | ESG factors can be used to identify companies with good corporate governance or companies with business models that are likely to face headwind or tailwind because of changes in structural trends |
| Personal Values | Incorporating ESG factors to align investments with personal values | ESG factors may revolve around investors’ values-based goals and represent a mean for investors to align their investments with their ethical, social, political or personal beliefs |
| Positive Impact | Incorporating ESG factors to make a difference in the world | ESG factors can be used to identify companies that provide solutions to environmental or social problems |
Why is ESG Investing Growing?
There are various reasons that give rise to the increasing popularity of ESG Investing and the utilisation of ESG factors to evaluate companies’ performance.
1. Alternative Sources of Energy
Technological advancement has made alternative sources of energy affordable and accessible. Therefore, it may be more economical for companies to switch to alternative or renewable sources of energy in the future. An over reliance on finite energy sources like crude oil or natural gases can create cost volatility for businesses should supply shortages occur.
2. Global Supply Chain Network
Multinational Corporations (MNCs) are corporate organizations that own or control the production of goods and services in at least one country other than its home country. The cross border coordination of business activities allow companies to capitalise on the competitive advantages that each market has to offer; low labour cost, availability of resources or abundance of skilled labour etc.
MNCs with operations in multiple markets may have to address issues like corruption practices, unfair labour practices and environmental degradation. The failure to respond to these problems may result in the costly disruption of the global supply chain network.
3. Demographic Shifts
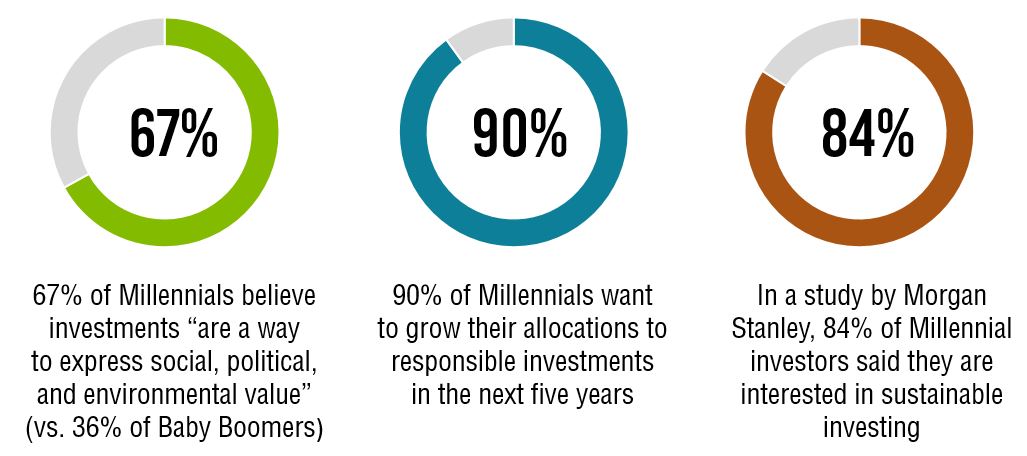
The Millennials and Generation-Xers will outnumber the Baby Boomers in the near future. The change in demographic structure will result in the seismic shift of the business, political and financial landscape.
Moreover, we are in the midst of the largest intergenerational wealth transfer in history. It is estimated that US$30 trillion in assets will be transferred from the Baby Boomers to their children over the next 30 to 40 years.6
The inheritors of the assets have different spending habits and investing decisions from their parental generation. The Bank of America Merrill Lynch predicts that Millennials could put between US$15 trillion and US$20 trillion into US domiciled ESG investments over the next two to three decades, which would nearly double the size of the entire US equity market.7
Figure 3: Highlights from MSCI ESG Research
4. Regulatory Changes and International Agreements
Following the Global Financial Crisis in 2008, there is an increased emphasis by regulators for businesses to improve their corporate governance to safeguard stakeholders’ interests. Good corporate governance is essential for the growth of the capital market ecosystem.8
According to the CFA Institute, many jurisdictions require a minimum level of governance-related disclosure and reporting from companies to provide stakeholders with material ESG information.9 Specifically, environmental-related disclosures are expected to be the focus of China’s new mandatory reporting regime, as the country strives to shape a sustainable future.
In addition, climate change is a reality and is universally acknowledged. Mitigation techniques include international agreements like the Paris Agreement and the Kyoto Protocol. The agreements aim to strengthen the participating nations’ abilities to combat climate change and environmental degradation by providing them with the necessary framework and resources to work with. MNCs with operations in the respective countries will be encouraged to contribute to the worldwide collective efforts in combating climate change.10
5. The Convergence of Social Norms
In the past, socially responsible norms may differ by countries or regions.
The advent of the Internet has created an interconnected world via the international media and social media network. Given its borderless nature, the Internet has the potential to alter the cultural and social norms of the world’s population. The convergence of social norms has resulted in the rise of social activism around the world.
Companies are encouraged to address ESG-related issues in order to take advantage of the network effect of social media to generate positive publicity or to avoid negative publicity amongst the global population.
The Rise of ESG ETFs
The first ESG theme Exchange Traded Fund (ETF), iShares MSCI USA ESG Select ETF, was launched in 2002. Since then, the number and variety of ESG ETFs/Exchange Traded Products (ETPs) have increased steadily, with 208 ESG ETFs/ETPs listed globally at the end of 2018.11
Total Asset under Management (AUM) for ESG ETFs/ETPs has reached US$22.47 billion at the end of 2018.
ESG ETFs are convenient investment vehicles for investors who are evaluating investments not only based on their financial goals, but also based on their personal values and social conscience. Instead of ciphering through market reports and news to identify companies with high ESG ratings, investors can now use ESG ETFs to gain exposure to their desired ESG investment strategy.
ETF Strategies to Achieve ESG Investment Objectives
ESG ETFs use a variety of strategies to achieve their ESG-focused investment objectives. Two common approaches used in ESG ETFs are the Exclusionary/Negative Screening and the Inclusionary/Positive Screening Strategies.
With the flourishment of the digital age, it is now fast and inexpensive for index providers and ETF issuers to gain access to ESG research and data. This helps to facilitate ESG integration into index construction and increase the potential for ETF issuers to launch a wide variety of ESG strategies ETFs.12
Figure 4: Illustration of Exclusionary/Negative Screening Process
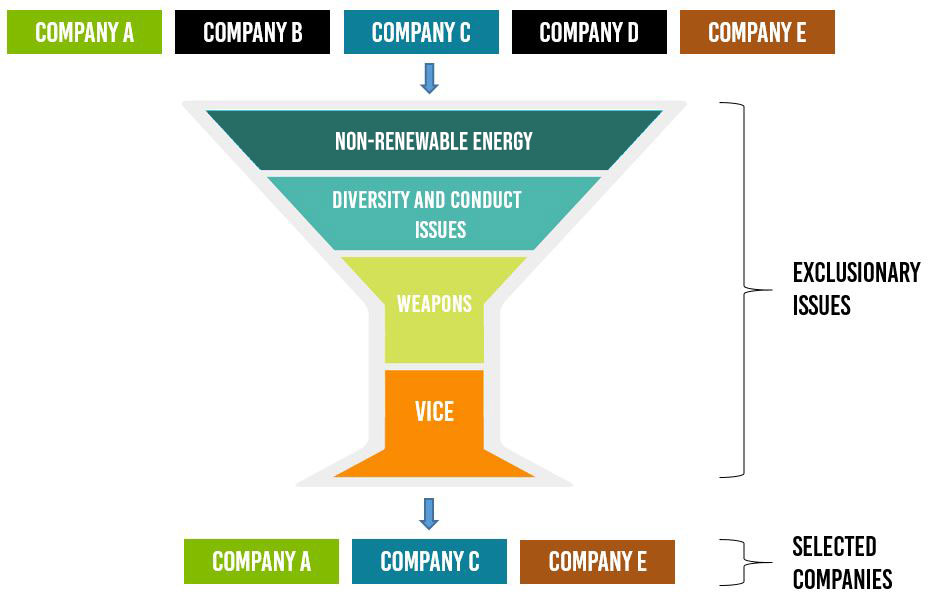
Figure 5: Illustration of Inclusionary/Positive Screening Process
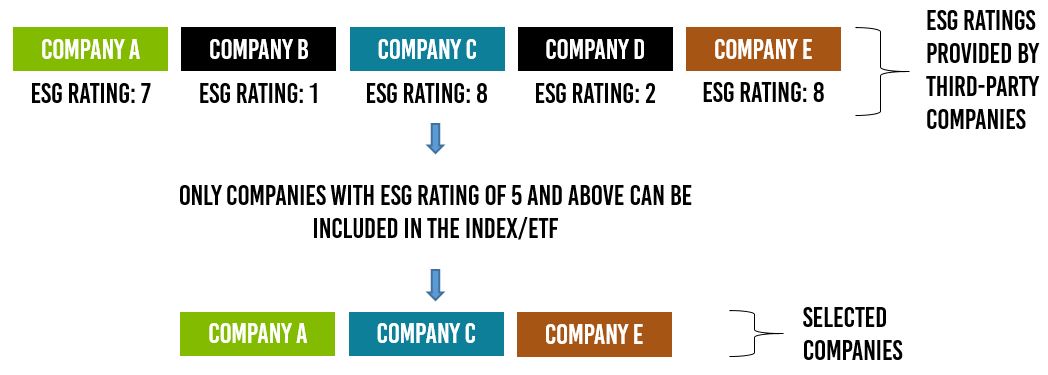
Some ESG ETFs may adopt an actively managed strategy to select its underlying stocks based on a set of underlying factors and ESG criteria.
Other types of ETFs that may adhere to ESG principles include impact or thematic investing ETFs. Examples of such ETFs include ETFs that revolve around certain themes like gender diversity or alternative energy.
Examples of ESG ETFs
| ETF | iShares ESG MSCI USA Leaders ETF | Xtrackers MSCI USA ESG Leaders Equity ETF | Vanguard ESG International Stock ETF | Vanguard ESG US Stock ETF |
| Ticker | SUSL | USSG | VSGX | ESGV |
| Exchange | NASDAQ | AMEX | AMEX | AMEX |
| AUM (US$) | 1.40 billion | 1.19 billion | 373.7 million | 519.10 million |
| Net Expense Ratio | 0.10% | 0.10% | 0.15% | 0.12% |
| Number of Holdings | 322 | 323 | 3420 | 1594 |
| Top 3 Holdings |
|
|
|
|
ETF Information is accurate as of 14 August 2019
Conclusion
Traditional fundamental metrics such as revenue, price-earnings ratio, sales growth and market capitalisation may not be adequate to evaluate the securities’ future performance and their suitability, given an investor’s needs, goals and risk tolerance.
A more comprehensive approach to investing should include the ESG factors to better evaluate an investor’s overall portfolio or financial strategy in today’s market conditions. A growing number of studies show a positive relationship between a company’s financial performance and its non-financial performance on ESG issues that are relevant to its sector and strategy.13
As structural change occurs and investors become more socially conscious, the number of ETFs adhering to ESG principles will continue to increase in the future.
Reference:
- [1] https://www.thebalance.com/a-short-history-of-socially-responsible-investing-3025578
- [2] https://www.ussif.org/files/US%20SIF%20Trends%20Report%202018%20Release.pdf
- [3] https://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/environmental-social-and-governance-esg-criteria.asp
- [4] https://www.msci.com/what-is-esg
- [5] https://www.washingtonpost.com/national/health-science/the-big-number-millennials-to-overtake-boomers-in-2019-as-largest-us-population-group/2019/01/25/a566e636-1f4f-11e9-8e21-59a09ff1e2a1_story.html
- [6] https://www.forbes.com/sites/nextavenue/2018/05/21/are-boomers-ready-to-make-the-greatest-wealth-transfer-in-history/#110085cf677d
- [7] https://www.msci.com/documents/10199/07e7a7d3-59c3-4d0b-b0b5-029e8fd3974b?source=post_page—————————
- [8] https://www.thenational.ae/business/we-must-tighten-up-corporate-governance-1.529729
- [9] https://www.cfainstitute.org/-/media/documents/article/position-paper/esg-disclosures-apac.ashx
- [10] https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/the-paris-agreement
- [11] https://etfgi.com/news/press-releases/2019/01/etfgi-reports-environmental-social-and-governance-esg-etfs-and-etps
- [12] https://www.ishares.com/us/literature/whitepaper/an-evolution-in-esg-indexing.pdf
- [13] https://www.forbes.com/sites/bobeccles/2017/10/25/total-societal-impact-is-the-key-to-improving-total-shareholder-return/#1fd90aa32113
Disclaimer
These commentaries are intended for general circulation. It does not have regard to the specific investment objectives, financial situation and particular needs of any person who may receive this document. Accordingly, no warranty whatsoever is given and no liability whatsoever is accepted for any loss arising whether directly or indirectly as a result of any person acting based on this information. Opinions expressed in these commentaries are subject to change without notice. Investments are subject to investment risks including the possible loss of the principal amount invested. The value of the units and the income from them may fall as well as rise. Past performance figures as well as any projection or forecast used in these commentaries are not necessarily indicative of future or likely performance. Phillip Securities Pte Ltd (PSPL), its directors, connected persons or employees may from time to time have an interest in the financial instruments mentioned in these commentaries. Investors may wish to seek advice from a financial adviser before investing. In the event that investors choose not to seek advice from a financial adviser, they should consider whether the investment is suitable for them.
The information contained in these commentaries has been obtained from public sources which PSPL has no reason to believe are unreliable and any analysis, forecasts, projections, expectations and opinions (collectively the “Research”) contained in these commentaries are based on such information and are expressions of belief only. PSPL has not verified this information and no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made that such information or Research is accurate, complete or verified or should be relied upon as such. Any such information or Research contained in these commentaries are subject to change, and PSPL shall not have any responsibility to maintain the information or Research made available or to supply any corrections, updates or releases in connection therewith. In no event will PSPL be liable for any special, indirect, incidental or consequential damages which may be incurred from the use of the information or Research made available, even if it has been advised of the possibility of such damages. The companies and their employees mentioned in these commentaries cannot be held liable for any errors, inaccuracies and/or omissions howsoever caused. Any opinion or advice herein is made on a general basis and is subject to change without notice. The information provided in these commentaries may contain optimistic statements regarding future events or future financial performance of countries, markets or companies. You must make your own financial assessment of the relevance, accuracy and adequacy of the information provided in these commentaries.
Views and any strategies described in these commentaries may not be suitable for all investors. Opinions expressed herein may differ from the opinions expressed by other units of PSPL or its connected persons and associates. Any reference to or discussion of investment products or commodities in these commentaries is purely for illustrative purposes only and must not be construed as a recommendation, an offer or solicitation for the subscription, purchase or sale of the investment products or commodities mentioned.
About the author
Mr. Joel Lim
ETF Specialist
Joel graduated from Singapore Institute of Management, University of London with a First Class Honours in Business. He was the recipient of SIM University of London’s Top Student Bronze Award in 2017 and was the worldwide examination topper for the “Financial Management” module in 2016. Joel was also commended by University of London for his excellent performance in the 2014 Examinations.
Joel is involved in ETF education, providing trading ideas and support to traders, dealers and fund managers. Joel also works closely with ETF issuers to educate retail investors about new ETFs during the Initial Offering Period.

 Gold ETFs for Singapore Retail Investors: Diversification and Inflation Protection
Gold ETFs for Singapore Retail Investors: Diversification and Inflation Protection  ETF Market Review: February Outlook Signals Strong Performance
ETF Market Review: February Outlook Signals Strong Performance  ETF Market Analysis: Oil & Hang Seng Set for January Gains
ETF Market Analysis: Oil & Hang Seng Set for January Gains  Buffer ETFs — What Are They and How Do They Work?
Buffer ETFs — What Are They and How Do They Work? 





