Trust fund
Table of Contents
Trust fund
There are various strategies to ensure your loved ones have a bright financial future. For instance, trust funds can be a powerful tool for preparing your children or grandkids for financial success in the future.
Trust funds are essential for designing and safeguarding your future, whether you want to preserve your wealth for retirement, save money for a child’s education, or just build a safety net for yourself and your loved ones.
What is a trust fund?
A trust fund is a legal body that holds assets or other property on behalf of an individual or group. A trustee is chosen when a trust is established and is responsible for managing trust funds.
Trust funds may include cash, bank accounts, real estate, stocks, companies, businesses, heirlooms, and other investments.
The grantor, who established the trust, chooses how and when to distribute the trust’s assets. These criteria typically depend on your age or stage of life. For instance, a beneficiary might receive a trust fund when they turn 21 or complete their college education.
Types of trust funds
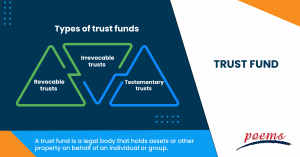
The primary types of trust funds are the following:
- Revocable trusts
Revocable trusts, often known as living trusts, are designed to avoid the probate process, which is the legal procedure for distributing an estate. Because it can be time-consuming, expensive, and public, using probate to handle your inheritance is not the greatest option for your heirs.
- Irrevocable trusts
Assets added to an irrevocable trust cannot be altered or revoked once it has been established, in contrast to revocable trusts. You are protected from potential estate taxes by placing assets in an irrevocable trust, which removes them from your estate because you have relinquished control over them.
The irrevocable life insurance trust, a kind of life insurance policy whose death benefits can be given to your beneficiaries or used to cover part of the expenses related to managing your estate without subjecting you to taxes, is a typical example.
- Testamentary trusts
Establishing a trust that takes effect after your death is feasible rather than setting one up and supporting it right away. This sort of trust, known as a testamentary trust, is established through the creation of a will, and the terms of the trust are specified in the will.
Trusts for minor children are frequently established using testamentary trusts as a tool. Although if the assets in a testamentary trust can be susceptible to probate, the freedom this kind of trust affords in selecting a trustee might exceed its expenses.
Benefits of a trust fund
Control over the administration of your assets is one of the benefits of a trust fund. Trust funds enable beneficiaries to avoid probate while ensuring that their assets are properly managed until they reach legal adulthood.
Trust funds may occasionally be used to dedicate money for specific expenses like medical or educational bills. The main advantage of being a Trust Fund beneficiary is the financial assistance you will get. Even though it may be upsetting to consider receiving anything from a loved one, a trust fund can benefit your financial condition.
Additionally, trust funds can assist you in avoiding the time-consuming and emotionally taxing probate court processes.
How does a trust fund work?
In a legally enforceable trust, the “trustor” gives the “beneficiary” the legal right to property or assets, which must be kept and used only for the beneficiary’s benefit.
The trustee operates the trust as a “miniature business,” managing the trustor’s assets until his passing. Following the trustee’s instructions as outlined in the trust agreement, the trustee, who controls the assets after the trustor passes away, distributes those assets to the beneficiaries.
Features of trust fund
The features of trust funds are:
- The grantor drafts a document defining the conditions of trust management and asset transfer. The agreement will detail the overall number of beneficiaries, their share of the trust’s assets, and more.
- A trust may hold a variety of assets, such as land, money in banks, investments in securities, cars, gold, and more. A trust account is a bank account component of a trust fund; it is very important to remember this.
- According to the form of trust, management differs. For instance, a living trust permits the grantor to use the trust’s assets. As a result, the grantor frequently also acts as a trustee. A new trustee is appointed after the grantor’s passing.
- To safeguard their riches, grantors frequently impose restrictions on their wills. A typical instance is when the agreement specifies that minor beneficiaries are not eligible to inherit until they turn 21. They can be granted a certain amount of money up until that point to cover things like living expenses and tuition costs.
- The kind of trust determines the assets’ ownership title. In irrevocable trusts, the grantor transfers ownership title, making the trust the sole owner of all purchases.
- Investments, such as the bank account of a trust fund, may continue to generate income and gains during its existence. It raises the worth of assets and necessitate tax payments from the trustee.
Frequently Asked Questions
A revocable trust can be revoked at any moment, whereas an irrevocable trust cannot be withdrawn after it has been created. With a revocable trust, the owner retains management and control over the asset even after it has been transferred. But, once an irrevocable trust has been established, the owner cannot use or possess it.
A person whose parents established a trust account from which they get benefits is referred to as a trust fund baby. The phrase “trust fund baby” has a bad reputation since it conjures up images of spoiled people who don’t have to work.
The main drawbacks of trusts include their perceived irrevocability, the loss of authority over assets, and the expenses. It is possible to make trusts revocable, although doing so typically negatively affects tax, estate duty, asset protection, and stamp duty.
A blind trust fund is a trust established by the grantor to give an impartial third-party trustee full control of their assets and investments. Once a trust has been established, neither the trustor nor the beneficiary controls how the trust fund is managed or how revenue is spent.
A unit trust fund is a fund that collects the money of investors and invests it into a broad portfolio of assets. Unit trusts often invest their money in various investments, with most of their holdings being bonds, equities, or a mix of the two.
Related Terms
- Settlement currency
- Federal funds rate
- Sovereign Wealth Fund
- New fund offer
- Commingled funds
- Taft-Hartley funds
- Umbrella Funds
- Late-stage funding
- Short-term fund
- Regional Fund
- In-house Funds
- Redemption Price
- Index Fund
- Fund Domicile
- Net Fund Assets
- Settlement currency
- Federal funds rate
- Sovereign Wealth Fund
- New fund offer
- Commingled funds
- Taft-Hartley funds
- Umbrella Funds
- Late-stage funding
- Short-term fund
- Regional Fund
- In-house Funds
- Redemption Price
- Index Fund
- Fund Domicile
- Net Fund Assets
- Forward Pricing
- Mutual Funds Distributor
- International fund
- Balanced Mutual Fund
- Value stock fund
- Liquid funds
- Focused Fund
- Dynamic bond funds
- Global fund
- Close-ended schemes
- Feeder funds
- Passive funds
- Gilt funds
- Balanced funds
- Tracker fund
- Actively managed fund
- Endowment Fund
- Target-date fund
- Lifecycle funds
- Hedge Funds
- Recovering funds
- Sector funds
- Open-ended funds
- Arbitrage funds
- Term Fed funds
- Value-style funds
- Thematic funds
- Growth-style funds
- Equity fund
- Capital preservation fund
Most Popular Terms
Other Terms
- Adjusted distributed income
- International securities exchanges
- Active Tranche
- Convertible Securities
- Synthetic ETF
- Physical ETF
- Initial Public Offering
- Buyback
- Secondary Sharing
- Bookrunner
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Payment Date
- Secondary Market
- Margin Requirement
- Mark-to-market
- Pledged Asset
- Yield Pickup
- Subordinated Debt
- Trailing Stops
- Treasury Stock Method
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Bullet Bonds
- Basket Trade
- Contrarian Strategy
- Exchange Control
- Notional Value
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Speculation
- Stub
- Trading Volume
- Going Long
- Pink sheet stocks
- Rand cost averaging
- Sustainable investment
- Stop-limit sell order
- Economic Bubble
- Ask Price
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Stock symbol
- Companion tranche
- Synthetic replication
Know More about
Tools/Educational Resources
Markets Offered by POEMS
Read the Latest Market Journal

Navigating the vast world of unit trusts can be daunting. With nearly 2000 funds available...

Predicting Trend Reversals with Candlestick Patterns for Beginners
Candlestick patterns are used to predict the future direction of price movements as they contain...

In the diverse and complex world of investing, unit trusts stand out as a popular...

Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Start trading on POEMS! Open a free account here! At a glance: Major indices continue...

Weekly Updates 15/4/24 – 19/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
In recent years, inflation has become a hot topic, evoking strong emotions as the cost...

Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
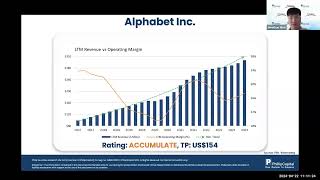
Source: eSignal, Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. In the heart of Japan’s economic landscape, the Nikkei 225...

Weekly Updates 8/4/24 – 12/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and...