Blockchain
Table of Contents
Blockchain
The term “blockchain technology” has likely been used with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin during the past few years. Most people believe Bitcoin and blockchain may be used interchangeably; however, this is not the case. Bitcoin is a currency that depends on blockchain technology to be safe, and blockchain technology can enable different applications connected to multiple sectors, including banking, manufacturing, supply chain, etc.
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent and tamper-proof record-keeping. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp and transaction data. This data can be anything of value, such as digital assets, contracts or identity information.
Blockchain technology is often compared to a digital ledger, as it allows for a secure and transparent way to track transactions. However, unlike a traditional ledger, blockchain technology is decentralised, meaning a single entity does not control it. This decentralisation makes blockchain technology particularly well-suited for applications that require trustless record-keeping, such as digital currencies.
Benefits of blockchain
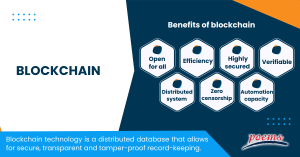
In an increasingly digitised environment, blockchain technology has various benefits:
- Open for all
One of the major benefits of blockchain technology is that anybody may use it and participate in it. Anyone can join the distributed network without requesting anyone’s permission.
- Zero censorship
Since trustworthy nodes are used for transaction validation and consensus methods that use smart contracts to authorise transactions, blockchain technology is likely immune from censorship since it is not under the authority of a single party.
- Highly secured
It employs a digital signature function to perform fraud-free transactions, making it difficult for other users to damage or alter an individual’s data without that user’s unique digital signature.
- Efficiency
Blockchain eliminates any third-party interference in transactions and eliminates errors, making the system more effective and quick. Settlement is facilitated and made easy.
- Verifiable
By employing zero-knowledge proof, which allows one party to demonstrate the accuracy of data to another party without disclosing any information about the data, blockchain technology is used to store data in a decentralised manner so that everyone can check the accuracy of the information.
- Distributed system
Normally, you need the authorization of regulatory bodies, such as a government or bank, to complete a transaction. With blockchain, transactions are carried out with the mutual consent of users, leading to more efficient, secure, and rapid transactions.
- Automation capacity
When the trigger’s conditions are satisfied, it is programmatic and may produce regular events, actions, and payments.
Types of blockchain
There are three types of blockchains:
- Public blockchains
They are decentralised and allow anyone to join and participate in the network.
- Private blockchains
They are permissioned and only allow authorised users to access the network.
- Consortium blockchains
It uses a unique strategy to address the organisation’s demands. In addition to initiating or receiving transactions, this blockchain also verifies transactions.
- Hybrid blockchains
It consists of a mixture of public and private blockchains where certain portions are under the authority of a single company, and others are made publicly accessible.
How does blockchain work?
Consider a blockchain as a transactional archive. Each block in a chain is immutably recorded via a peer-to-peer network and “chained” to the one before it. Cryptographic security and assurance technology gives each transaction a distinct identifier—or digital fingerprint—.
The chain is forged with trust, accountability, openness, and security. This promotes a phenomenon known as third-party, consensus-based confidence, which enables a wide range of organisations and business partners to access and exchange data.
Blocks, nodes, and miners are the three key components of the proof-of-work blockchain technology.
This innovative solution may be used by any company that needs a safe, up-to-date record of transactions that can be shared. There is no center element of risk because everything is kept across several locations, improving security and availability.
Blockchain use cases and applications.
There are several different blockchain use cases and applications that are being developed and implemented across a variety of industries. Some of the most popular use cases include:
- Supply chain management
Supply chain management is one of blockchain technology’s most commonly cited use cases. Businesses may improve supply chain visibility and guarantee that their products originate from the locations they claim by utilising blockchain to trace the flow of goods and resources. This can help to combat issues such as counterfeit goods and human trafficking.
- Asset management
Asset management is another key area where blockchain is being used. By tokenizing assets on a blockchain, businesses can streamline the process of buying, selling, and transferring assets. This can reduce costs and increase efficiency.
- Identity management
Identity management is another important blockchain application. By using blockchain to store and manage identity data, businesses can provide their customers with a secure and convenient way to login and access their accounts. This can help to reduce fraud and improve customer satisfaction.
- Data management
Data management is another key area where blockchain is being used. By storing data on a blockchain, businesses can ensure that it is secure and tamper-proof. This can help to improve data security and protect against data breaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bitcoin is a digital asset and a payment system invented by Satoshi Nakamoto. Blockchains are distributed public ledgers where transactions are recorded and cryptographically validated by network nodes.
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies may exist because of blockchain technology. An electronic log of all bitcoin transactions is known as a blockchain. It keeps expanding as fresh recordings are added to “finished” blocks.
Each block includes transaction information, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the one before it. The blockchain is used by Bitcoin nodes to distinguish between valid transactions and efforts to spend previously spent currencies again.
A private blockchain is a blockchain that is permissioned. So, only those with the correct permissions can access it. In contrast, a public blockchain is a blockchain that anyone can access. Private blockchains are often used within businesses, while public blockchains are often used for cryptocurrency.
A blockchain platform is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that uses a decentralised network of computers to manage and record transactions. This platform is secure and tamper-resistant, making it well-suited for managing digital assets. Blockchain platforms can be used to create or support new applications. In either case, they can streamline processes and reduce costs.
Different industries are using blockchain in different ways. For example, the banking industry is using blockchain to speed up the process of processing payments and to reduce the costs associated with processing transactions.
The healthcare industry uses blockchain to securely store patient health records and track medical supplies’ movement. The retail industry uses blockchain to track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain and prevent counterfeiting.
Five fundamental elements of a blockchain network include the following:
- Decentralised ledger
- P2P: Peer-to-peer network
- Consensus Mechanism
- Cryptography
- Virtual Machine
Related Terms
- Secondary Market
- Subordinated Debt
- Basket Trade
- Notional Value
- Speculation
- Quiet period
- Purchasing power
- Interest rates
- Plan participant
- Performance appraisal
- Anaume pattern
- Commodities trading
- Swing trading
- Interest rate risk
- Equity Trading
- Secondary Market
- Subordinated Debt
- Basket Trade
- Notional Value
- Speculation
- Quiet period
- Purchasing power
- Interest rates
- Plan participant
- Performance appraisal
- Anaume pattern
- Commodities trading
- Swing trading
- Interest rate risk
- Equity Trading
- Adverse Excursion
- Booked Orders
- Bracket Order
- Bullion
- Trading Indicators
- Grey market
- Intraday trading
- Futures trading
- Broker
- Head-fake trade
- Demat account
- Price priority
- Day trader
- Threshold securities
- Online trading
- Quantitative trading
- Insider trading
- Ex-dividend date
- Equity Volume
- Downtrend
- Derivatives
Most Popular Terms
Other Terms
- Adjusted distributed income
- International securities exchanges
- Settlement currency
- Federal funds rate
- Active Tranche
- Convertible Securities
- Synthetic ETF
- Physical ETF
- Initial Public Offering
- Buyback
- Secondary Sharing
- Bookrunner
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Payment Date
- Margin Requirement
- Mark-to-market
- Pledged Asset
- Yield Pickup
- Trailing Stops
- Treasury Stock Method
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Bullet Bonds
- Contrarian Strategy
- Exchange Control
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Stub
- Trading Volume
- Going Long
- Pink sheet stocks
- Rand cost averaging
- Sustainable investment
- Stop-limit sell order
- Economic Bubble
- Ask Price
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Stock symbol
- Companion tranche
- Synthetic replication
- Bourse
- Beneficiary
- Witching Hour
Know More about
Tools/Educational Resources
Markets Offered by POEMS
Read the Latest Market Journal

Navigating the vast world of unit trusts can be daunting. With nearly 2000 funds available...

Predicting Trend Reversals with Candlestick Patterns for Beginners
Candlestick patterns are used to predict the future direction of price movements as they contain...

In the diverse and complex world of investing, unit trusts stand out as a popular...

Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Start trading on POEMS! Open a free account here! At a glance: Major indices continue...

Weekly Updates 15/4/24 – 19/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
In recent years, inflation has become a hot topic, evoking strong emotions as the cost...

Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
Source: eSignal, Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. In the heart of Japan’s economic landscape, the Nikkei 225...

Weekly Updates 8/4/24 – 12/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and...












