Green bonds
Table of Contents
Green bonds
The market for green bonds is expanding owing to a variety of factors. The necessity of funding projects that have a favorable influence on the environment is becoming more apparent. Investor demand for green bonds has increased as a result of this.
Additionally, governments and supranational organizations increasingly use green bonds to finance climate-related projects.
What is a green bond?
Green bonds are a type of debt instrument used to finance environmental projects. The proceeds from the sale of green bonds are used to fund projects with a positive environmental impact, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction.
Green bonds are a type of debt instrument specifically earmarked for financing environmental projects. As such, they represent a key tool for mobilizing private capital for climate-related investments. Given the importance of these bonds in promoting sustainable development, it is critical to ensure that they are issued transparently and accountably.
Types of green bonds
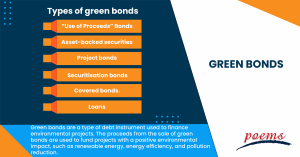
Some of the categories of green bonds that can be offered on the market are listed below:
- “Use of Proceeds” Bonds
This financial instrument is used to fund environmental initiatives, but the lenders may access the issuer’s other assets in the liquidation scenario. The same credit rating as the issuer’s other bonds applies to these instruments.
- Asset-backed securities (ABS) or “Use of Proceeds” Revenue Bonds
These bonds can be used to refinance or fund green projects, but the debt is secured by streams of income that the issuer collects, such as taxes or fees. When issuing green bonds, state and local organizations could choose to use this kind of framework.
- Project bonds
This kind of bond only applies to a certain underlying green project. Therefore, investors’ liability is restricted to the project’s assets.
- Securitisation bonds
These debt instruments consist of a collection of projects merged into one debt portfolio, including bondholders having access to the assets supporting the whole collection of projects.
- Covered bonds.
This financial instrument entails funding a collection of eco-friendly initiatives known as the “covered pool”. Investors can seek redress from the issuer in this situation, but if the issuer fails to fulfill debt payments, bondholders can seek redress from the covered pool.
- Loans
Loans for green projects can be either unsecured or secured. Lenders have complete recourse to the borrower’s assets while making unsecured loans. When making a secured loan, the lender may have some partial recourse against the borrower and the collateral.
Main uses of green bonds
Governments, corporations, or financial institutions can issue green bonds. They are typically used to finance long-term projects with a horizon of 5-10 years.
The green bonds market has grown rapidly in recent years, with over $250 billion worth of green bonds being issued in 2017 alone. This growth is expected to continue as more investors seek to invest in environmentally friendly projects.
Advantages of green bonds
The key advantages of green bonds include the following:
- Green bonds can help to unlock new sources of capital for climate-related projects.
- They can assist in letting the market know how committed the issuer is to tackling climate-related problems.
- Green bonds can help to generate positive publicity for the issuer.
- They can help to attract new investors who are interested in climate-related issues.
- Green bonds can help to create a market for climate-related projects.
- They can help to increase transparency and disclosure around climate-related issues.
Challenges of green bonds
While the concept of green bonds has been around for several years, the market for green bonds has only begun to develop in recent years. Several challenges need to be addressed for the green bond market to grow.
One of the key challenges is the lack of a standardized definition for green bonds. Another challenge is the lack of data and transparency around green bond issuance. This lack of data makes it difficult for investors to assess the risks and opportunities associated with investing in green bonds.
Despite these challenges, the green bond market is expected to grow in the coming years. The necessity to fund environmental projects and investors’ desire to support such projects contribute to this expansion.
Frequently Asked Questions
Governments and corporations issue green bonds to raise capital for environmental projects. Investors who purchase green bonds receive interest payments from the issuer, and the principal is returned at maturity. The terms of green bonds are similar to traditional bonds, but the proceeds must be used for eligible environmental projects.
Green bonds can be an important tool for funding the transition to a low-carbon economy. By directing capital to environmental projects, green bonds can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote the use of renewable energy, and protect natural resources.
Green bonds are a debt instrument specifically used to finance environmental projects. Blue bonds, on the other hand, are a type of debt instrument used to finance projects that positively impact the oceans.
The proceeds from the sale of green bonds are used to fund projects with a positive environmental impact, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction. In contrast, the proceeds from the sale of blue bonds are used to fund projects that improve the health of the oceans, such as marine conservation, sustainable fisheries, and pollution reduction.
The global green bonds market has been growing rapidly in recent years, and the forecasted market value is anticipated to rise to USD 615 billion by 2025. Governments and supranational organizations like the World Bank issue most green bonds.
In the upcoming years, the market for green bonds is anticipated to expand. This will be driven by the increasing awareness of the need to finance projects with a positive environmental impact and the continuing efforts of governments and supranational organizations to finance climate-related projects.
The first step in verifying a green bond is to check that a reputable institution has issued it. The issuing institution should be a member of the Climate Bonds Initiative (CBI), an international not-for-profit organization that promotes the development of the green bonds market.
Once you have verified that a reputable institution has issued the bond, you should check the documentation to see what the bond is financing. The documentation should contain a clear and concise description of the project and the expected environmental impacts. It should be treated with caution if the documentation is unclear or incomplete.
Finally, you should check to see if a third party has independently verified the green bond. The Climate Bonds Initiative maintains a list of approved verifiers, which can be found on its website. If an approved verifier has not verified the bond you are considering, it is best to proceed cautiously.
Governments, companies, or financial institutions can issue green bonds. For example, the World Bank has issued green bonds to finance climate change mitigation and adaptation projects, and the City of London has issued green bonds to finance installing solar panels on public buildings.
Green bonds are one way to encourage investment in environmentally friendly projects. By directing funds to these projects, green bonds can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, pollution, and other environmental impacts.
Related Terms
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Bullet Bonds
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Companion tranche
- Savings bond calculator
- Variable-Interest Bonds
- Warrant Bonds
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Bullet Bonds
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Companion tranche
- Savings bond calculator
- Variable-Interest Bonds
- Warrant Bonds
- Eurobonds
- Emerging Market Bonds
- Serial bonds
- Equivalent Taxable Yield
- Equivalent Bond Yield
- Performance bond
- Death-Backed Bonds
- Joint bond
- Obligation bond
- Bond year
- Overhanging bonds
- Bond swap
- Concession bonds
- Adjustable-rate mortgage
- Bondholder
- Yen bond
- Liberty bonds
- Premium bond
- Gold bond
- Reset bonds
- Refunded bond
- Additional bonds test
- Corporate bonds
- Coupon payments
- Authority bond
- Clean price
- Secured bonds
- Revenue bonds
- Perpetual bonds
- Municipal bonds
- Quote-Driven Market
- Debenture
- Fixed-rate bond
- Zero-coupon bond
- Convexity
- Compounding
- Parallel bonds
- Junk bonds
- Average maturity
- Investment grade bonds
- Convertible Bonds
Most Popular Terms
Other Terms
- International securities exchanges
- Settlement currency
- Federal funds rate
- Active Tranche
- Convertible Securities
- Synthetic ETF
- Physical ETF
- Initial Public Offering
- Buyback
- Secondary Sharing
- Bookrunner
- Payment Date
- Secondary Market
- Margin Requirement
- Mark-to-market
- Pledged Asset
- Yield Pickup
- Subordinated Debt
- Trailing Stops
- Treasury Stock Method
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Basket Trade
- Contrarian Strategy
- Exchange Control
- Notional Value
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Speculation
- Stub
- Trading Volume
- Going Long
- Pink sheet stocks
- Rand cost averaging
- Sustainable investment
- Stop-limit sell order
- Economic Bubble
- Ask Price
- Stock symbol
- Synthetic replication
- Bourse
- Beneficiary
- Witching Hour
- Widow and Orphan stock
- Public Float
- Closing Price
- Reverse stock splits
- Quiet period
- Prepayment risk
- Interpolation
- Homemade leverage
Know More about
Tools/Educational Resources
Markets Offered by POEMS
Read the Latest Market Journal

Predicting Trend Reversals with Candlestick Patterns for Beginners
Candlestick patterns are used to predict the future direction of price movements as they contain...

In the diverse and complex world of investing, unit trusts stand out as a popular...

Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Start trading on POEMS! Open a free account here! At a glance: Major indices continue...

Weekly Updates 15/4/24 – 19/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
In recent years, inflation has become a hot topic, evoking strong emotions as the cost...

Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
Source: eSignal, Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. In the heart of Japan’s economic landscape, the Nikkei 225...

Weekly Updates 8/4/24 – 12/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and...

What Makes Forex Trading Attractive?
In a world where the click of a button can send goods across oceans and...