Variable-Interest Bonds
Table of Contents
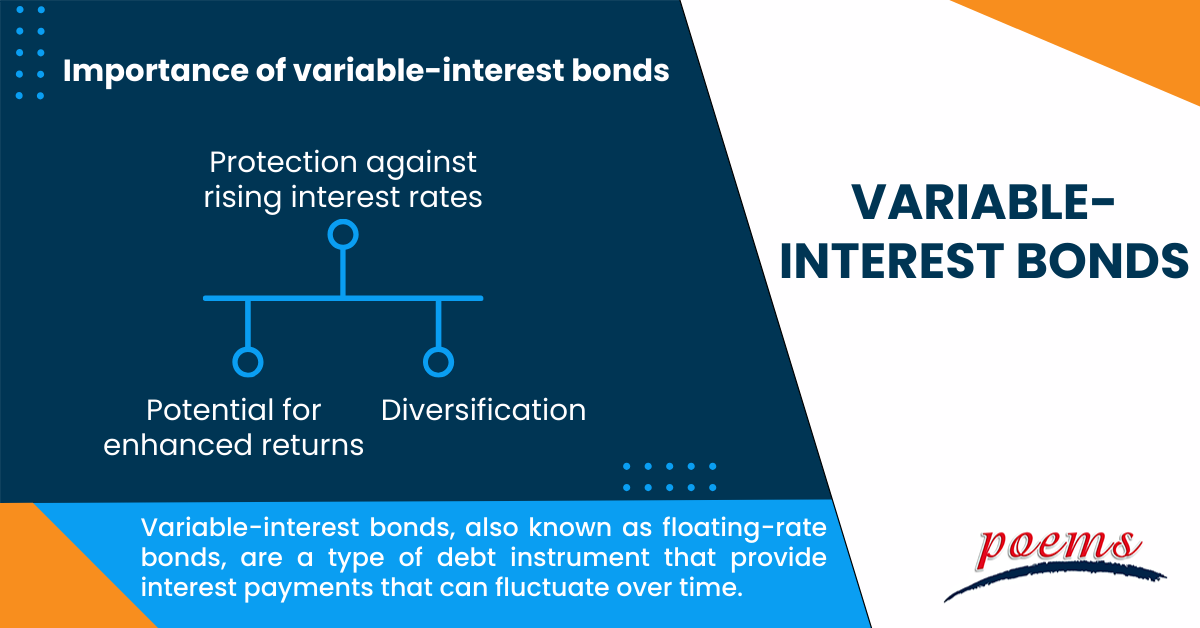
Variable-Interest Bonds
When it comes to investing, bonds have always been a popular choice for individuals seeking a stable and predictable income stream. Among the various types of bonds available, variable-interest bonds stand out as a unique investment instrument that offers flexibility and the potential for increased returns. Variable-interest bonds offer a unique investment opportunity for investors seeking flexibility, potential for enhanced returns, and protection against rising interest rates. By understanding the working, importance, and examples of variable-interest bonds, investors can make informed decisions aligned with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
What are variable-interest bonds?
Variable-interest bonds, also known as floating-rate bonds, are a type of debt instrument that provide interest payments that can fluctuate over time. Unlike traditional fixed-interest bonds, where the interest rate remains constant throughout the bond’s life, variable-interest bonds offer interest payments that are linked to a reference rate, As these reference rates change, the interest payments on variable-interest bonds adjust accordingly. This feature makes variable-interest bonds an appealing option for individuals seeking stable and predictable income streams while still being responsive to interest rate movements.
Understanding variable-interest bonds
Variable-interest bonds are designed to provide investors with a hedge against interest rate fluctuations. When interest rates rise, the interest payments on these bonds increase, thereby protecting investors from losing out on higher returns. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the interest payments on variable-interest bonds decrease, which can be advantageous for investors seeking to capitalise on declining interest rates.
These bonds typically have a specified spread or margin above the reference rate, which determines the interest rate paid to bondholders. For example, a variable-interest bond with a spread of 2% above LIBOR will yield an interest rate equal to the prevailing LIBOR rate plus 2%. This spread acts as a premium for taking on the risk associated with the variable interest payments.
Working of variable-interest bonds
The working of variable-interest bonds is based on a dynamic interest rate structure that adjusts periodically, providing investors with flexibility and potential returns that align with market conditions. Variable-interest bonds function based on a predetermined formula that calculates the interest payments at specified intervals, such as quarterly or semi-annually. The formula involves adding the reference rate to the predetermined spread to determine the bond’s interest rate for the payment period.
The frequency at which the interest rate is adjusted varies depending on the bond’s terms and conditions. There is typically a reset period during which the interest rate is recalculated based on the prevailing reference rate. This can range from as short as one day to several months, depending on the specific bond.
It is important to note that variable-interest bonds typically have a reset period, during which the interest rate is recalculated based on the prevailing reference rate. This reset period can range from as short as one day to as long as several months, depending on the bond’s terms and conditions.
Importance of variable-interest bonds
- Protection against rising interest rates: Variable-interest bonds offer investors a way to safeguard their income from the negative effects of rising interest rates. As interest rates increase, the interest payments on these bonds rise accordingly, ensuring that investors receive higher returns compared to fixed-interest bonds.
- Potential for enhanced returns: In a low-interest-rate environment, variable-interest bonds can provide an opportunity for higher returns when interest rates eventually rise. As rates increase, the interest payments on these bonds also rise, potentially outperforming fixed-interest bonds over time.
- Diversification: Including variable-interest bonds in an investment portfolio can provide diversification benefits. Their performance is often uncorrelated with other asset classes, such as stocks or fixed-interest bonds, making them a valuable addition for risk-conscious investors looking to balance their portfolios.
Examples of variable-interest bonds
Variable-interest bonds offer investors the opportunity to benefit from changing interest rates, providing flexibility and potential for increased returns. Some examples are:
1. US Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS)
TIPS are a type of variable-interest bond issued by the US Treasury. They offer investors protection against inflation by adjusting the principal value of the bond and the interest payments based on changes in the Consumer Price Index, or CPI. This adjustment ensures that the purchasing power of the bond’s future cash flows is maintained, making TIPS an attractive investment during inflationary periods.
2. Singapore Savings Bonds (SSB)
SSBs are a type of variable-interest bond issued by the Singapore government. They provide retail investors with a safe and flexible investment option. The interest rates on SSBs are reviewed and adjusted every six months, allowing investors to benefit from changes in interest rates over time. SSBs offer attractive yields compared to traditional savings accounts and can be a suitable choice for Singaporean investors seeking low-risk investments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Interest on traditional bonds is typically fixed, meaning it remains constant throughout the bond’s life. However, variable-interest bonds offer interest payments that can fluctuate based on changes in a reference rate, providing investors with more flexibility.
Variable-interest bonds offer protection against rising interest rates, potential for enhanced returns, and diversification benefits. These advantages make them appealing to investors looking to mitigate interest rate risk and seek higher yields.
One potential disadvantage of variable-interest bonds is the uncertainty surrounding future interest payments. As interest rates fluctuate, the income generated by these bonds can be unpredictable. Additionally, variable-interest bonds may carry higher credit risk compared to fixed-interest bonds.
A variable-rate demand bond is a type of municipal bond that allows investors to demand repayment of the bond’s principal at periodic intervals. The interest rate on these bonds is typically reset at predetermined intervals, providing investors with flexibility and liquidity.
The choice between variable and fixed interest depends on an investor’s risk appetite, investment objectives, and market conditions. Variable interest can offer potential benefits during periods of declining interest rates or inflation, while fixed interest provides stability and predictability. It is important for investors to evaluate their individual circumstances before making a decision.
Related Terms
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Bullet Bonds
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Companion tranche
- Savings bond calculator
- Warrant Bonds
- Eurobonds
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Bullet Bonds
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Companion tranche
- Savings bond calculator
- Warrant Bonds
- Eurobonds
- Emerging Market Bonds
- Serial bonds
- Equivalent Taxable Yield
- Equivalent Bond Yield
- Performance bond
- Death-Backed Bonds
- Joint bond
- Obligation bond
- Bond year
- Overhanging bonds
- Bond swap
- Concession bonds
- Adjustable-rate mortgage
- Bondholder
- Yen bond
- Liberty bonds
- Premium bond
- Gold bond
- Reset bonds
- Refunded bond
- Additional bonds test
- Corporate bonds
- Coupon payments
- Authority bond
- Clean price
- Secured bonds
- Revenue bonds
- Perpetual bonds
- Municipal bonds
- Quote-Driven Market
- Debenture
- Fixed-rate bond
- Zero-coupon bond
- Convexity
- Compounding
- Parallel bonds
- Junk bonds
- Green bonds
- Average maturity
- Investment grade bonds
- Convertible Bonds
Most Popular Terms
Other Terms
- Adjusted distributed income
- International securities exchanges
- Settlement currency
- Federal funds rate
- Active Tranche
- Convertible Securities
- Synthetic ETF
- Physical ETF
- Initial Public Offering
- Buyback
- Secondary Sharing
- Bookrunner
- Payment Date
- Secondary Market
- Margin Requirement
- Mark-to-market
- Pledged Asset
- Yield Pickup
- Subordinated Debt
- Trailing Stops
- Treasury Stock Method
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Basket Trade
- Contrarian Strategy
- Exchange Control
- Notional Value
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Speculation
- Stub
- Trading Volume
- Going Long
- Pink sheet stocks
- Rand cost averaging
- Sustainable investment
- Stop-limit sell order
- Economic Bubble
- Ask Price
- Stock symbol
- Synthetic replication
- Bourse
- Beneficiary
- Witching Hour
- Widow and Orphan stock
- Public Float
- Closing Price
- Reverse stock splits
- Quiet period
- Prepayment risk
- Interpolation
Know More about
Tools/Educational Resources
Markets Offered by POEMS
Read the Latest Market Journal

Navigating the vast world of unit trusts can be daunting. With nearly 2000 funds available...

Predicting Trend Reversals with Candlestick Patterns for Beginners
Candlestick patterns are used to predict the future direction of price movements as they contain...

In the diverse and complex world of investing, unit trusts stand out as a popular...

Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Start trading on POEMS! Open a free account here! At a glance: Major indices continue...

Weekly Updates 15/4/24 – 19/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
In recent years, inflation has become a hot topic, evoking strong emotions as the cost...

Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
Source: eSignal, Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. In the heart of Japan’s economic landscape, the Nikkei 225...

Weekly Updates 8/4/24 – 12/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and...












