Arbitrage
Table of Contents
Arbitrage
Arbitrage can be used whenever a stock, commodity, or unit of currency can be purchased at one price on one market while simultaneously being sold at a higher price on another. The situation allows the trader to gain without taking any risks.
Arbitrage prevents prices from deviating materially from fair value over an extended period. Technology advancements have made it very challenging to profit from pricing mistakes in the market.
Many traders have automated trading programs configured to track changes in similar financial instruments. Any ineffective pricing structures are typically addressed quickly, often within a few seconds, and the opportunity is lost.
What is arbitrage?
Arbitrage is the simultaneous buying and selling of the same asset on different markets. The objective is to profit from slight changes in the asset’s quoted price. It benefits from brief fluctuations in the price of equivalent or comparable financial products offered in different markets or formats. Market inefficiencies cause arbitrage, which both take advantage of and correct them.
Arbitrage is the simultaneous acquisition and disposal of an asset in various markets to take advantage of minute price differences. Trades in stocks, commodities, and currencies are all examples of arbitrage. Arbitrage makes use of certain market inefficiencies.
Types of arbitrage
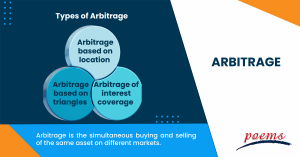
The following forms are the types of arbitrage:
- Arbitrage based on location
The use of a small differential in the exchange rates of two financial institutions by an investor is known as locational arbitrage. It is predicated on making profitable purchases from one bank and selling to other banks for the benefit of the investors.
- Arbitrage based on triangles
The three separate currencies must be sold and bought as part of the complicated triangle arbitrage. The idea behind arbitrage is the same since it accounts for minute differences in the exchange rate.
- Arbitrage of interest coverage
The complex interest coverage arbitrage method of risk-free profit making entails investing in the currency at a higher interest rate and protecting against negative currency fluctuations and devaluations.
How does arbitrage work?
In its most basic form, arbitrage is claimed to be risk-free and relies on the ability to execute both sides of the trade at the appropriate moment.
This can be demonstrated by taking into account the fact that the majority of financial goals are met by buying low and selling high. But even if someone buys an asset they believe to be undervalued; the price could rise or fall. For example, it could make someone assume a stock is low priced when it is overvalued.
With arbitrage, the “buy low, sell high” opportunity frequently arises simultaneously, leading to the idea of a deal with no risk. Due to the fact that prices quickly and effectively reflect information, arbitrage is difficult to find within a single nation.
Importance of arbitrage
Arbitrage is crucial for promoting market liquidity. And the amount of sales and purchases made inside the market rises due to this activity.
Additionally, the market sells the high-priced security when arbitrageurs buy it, driving the price of the lower-priced security up. As a result, the gap between identical assets gets smaller, and the market’s overall efficiency rises.
Arbitrage traders improve the financial markets’ effectiveness while working to increase their profits. The price discrepancies between identical or comparable assets get smaller when they are bought and sold. While the higher-priced assets are sold off, the lower-priced assets are bid up. Arbitrage corrects pricing inefficiencies in this way while also bringing more liquidity to the market.
What are some examples of arbitrage?
The practice of buying and selling shares of stocks, commodities, or currencies on various markets to profit from the inevitable fluctuations in their prices from minute to minute is known as arbitrage.
However, other trading activities can sometimes be described using the term arbitrage. One tactic well-liked among hedge fund investors is merger arbitrage, which entails purchasing companies’ shares before a merger has been announced or is anticipated.
Frequently Asked Questions
Arbitrage trading is an alternative investment strategy that entails buying and selling stocks, commodities, and currencies in various markets or cryptocurrency exchanges while swiftly exploiting the minute price differences to make profits.
Arbitrage trading is an opportunity in the financial markets that rewards knowledgeable investors and institutions with high volume to optimize the opportunity afforded by price discrepancies and profit from minute variations in identical or comparable assets across markets.
It is a method that takes advantage of differing pricing for the same item that is trading on another exchange and is known as arbitrage crypto. In plain language, a trader might profit from slight discrepancies or imbalances in the price valuation of an item listed on two different exchanges.
Arbitrage trading is recognized to occur regularly in the forex market but is also common in stock markets. In general, only stocks traded in various currencies and listed on multiple exchanges are eligible for arbitrage in the stock market.
Market liquidity is produced by arbitrage trading. It facilitates an equilibrium required for markets to operate fairly when comparable or equitable assets are valued differently.
Large-volume arbitrage trades raise the value of a stock or asset undervalued in one area, exchange, or market by making large purchases. The same stock overvalued in one market is dumped, which lowers its price. The price of dual-listed stocks is equalised in this way.
It is a well-known tactic that seeks to profit from the price difference between a spot market and a futures contract is spot-futures arbitrage, also is referred to as cash-and-carry arbitrage. The low risk involved is the main benefit of spot-futures arbitrage, which is descended from the family of market-neutral methods.
Spot-futures arbitrage is a traditional and straightforward trading strategy distinguished by its simplicity and low risk. In essence, traders keep an eye on the basis, which is the difference between the underlying asset’s spot market price and futures price, and they enter a transaction if the basis is higher than the trade costs.
Related Terms
- Payment Date
- Treasury Stock Method
- Reverse stock splits
- Ticker
- Restricted strict unit
- Gordon growth model
- Stock quotes
- Shadow Stock
- Margin stock
- Dedicated Capital
- Whisper stock
- Voting Stock
- Deal Stock
- Microcap stock
- Capital Surplus
- Payment Date
- Treasury Stock Method
- Reverse stock splits
- Ticker
- Restricted strict unit
- Gordon growth model
- Stock quotes
- Shadow Stock
- Margin stock
- Dedicated Capital
- Whisper stock
- Voting Stock
- Deal Stock
- Microcap stock
- Capital Surplus
- Multi-bagger Stocks
- Shopped stock
- Secondary stocks
- Screen stocks
- Quarter stock
- Orphan stock
- One-decision stock
- Repurchase of stock
- Stock market crash
- Half stock
- Stock options
- Stock split
- Foreign exchange markets
- Stock Market
- FAANG stocks
- Unborrowable stock
- Joint-stock company
- Over-the-counter stocks
- Watered stock
- Zero-dividend preferred stock
- Bid price
- Authorised shares
- Auction markets
- Market capitalisation
- Market capitalisation rate
- Garbatrage
- Autoregressive
- Stockholder
- Penny stock
- Noncyclical Stocks
- Hybrid Stocks
- Large Cap Stocks
- Mid Cap Stocks
- Common Stock
- Preferred Stock
- Small Cap Stocks
- Earnings Per Share (EPS)
- Diluted Earnings Per Share
- Dividend Yield
- Cyclical Stock
- Blue Chip Stocks
- Averaging Down
Most Popular Terms
Other Terms
- Physical ETF
- Initial Public Offering
- Buyback
- Secondary Sharing
- Bookrunner
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Secondary Market
- Margin Requirement
- Mark-to-market
- Pledged Asset
- Yield Pickup
- Subordinated Debt
- Trailing Stops
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Bullet Bonds
- Basket Trade
- Contrarian Strategy
- Exchange Control
- Notional Value
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Speculation
- Stub
- Trading Volume
- Going Long
- Pink sheet stocks
- Rand cost averaging
- Sustainable investment
- Stop-limit sell order
- Economic Bubble
- Ask Price
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Stock symbol
- Companion tranche
- Synthetic replication
- Bourse
- Beneficiary
- Witching Hour
- Widow and Orphan stock
- Public Float
- Closing Price
- Quiet period
Know More about
Tools/Educational Resources
Markets Offered by POEMS
Read the Latest Market Journal

Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Start trading on POEMS! Open a free account here! At a glance: Major indices continue...

Weekly Updates 15/4/24 – 19/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
In recent years, inflation has become a hot topic, evoking strong emotions as the cost...

Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
Source: eSignal, Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. In the heart of Japan’s economic landscape, the Nikkei 225...

Weekly Updates 8/4/24 – 12/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and...

What Makes Forex Trading Attractive?
In a world where the click of a button can send goods across oceans and...

Weekly Updates 1/4/24 – 5/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

How to soar higher with Positive Carry!
As US Fed interest rates are predicted to rise 6 times this year, it’s best...












