Acquisition
Table of Contents
Acquisition
In recent years, there has been an upsurge in the number of companies acquired by larger firms. This has led to an increase in the amount of money spent on acquisitions and the number of people employed in the acquisition process.
Acquisitions can be a complex and time-consuming process involving many different parties, but they can be a great way for companies to grow and expand their operations. However, they can also be a risky proposition, and it is important to make sure that all of the necessary due diligence is conducted before completing a deal.
What is an acquisition?
The acquisition is the process of obtaining something, usually through purchase or conquest. In business, the acquisition is often used to refer to the purchase of a company by another company. This can be done through a merger, in which the two companies combine to form a new entity, or through a takeover, in which one company buys out the other. Acquisitions can benefit both the buyer and seller, as they can provide access to new markets, technologies, and economies of scale.
Benefits of acquisitions
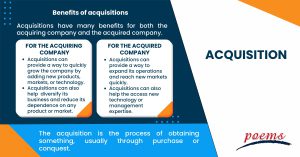
Acquisitions have many benefits for both the acquiring company and the acquired company. For the acquiring company, acquisitions can provide a way to quickly grow the company by adding new products, markets, or technology.
Acquisitions can also help the acquiring company diversify its business and reduce its dependence on any product or market. For the acquired company, acquisitions can provide a way to expand its operations and reach new markets quickly.
Acquisitions can also help the acquired company access new technology or management expertise.
Challenges with acquisitions
Acquiring another company can be a challenge for many reasons.
- The first challenge is finding the right company to acquire. The acquirer must find a company that is a fit both strategically and culturally. The acquirer also needs to be sure that the target company is well-managed and has a good track record.
- The second challenge is integrating the two companies successfully. The acquirer must ensure that the target company’s employees are integrated into the acquirer’s organization. The acquirer must also ensure that the target company’s products and services are integrated into the acquirer’s offerings.
- The third challenge is making sure that the acquisition is financially successful. The acquirer must ensure that the target company generates enough revenue to cover the acquisition costs. The acquirer also needs to make sure that the target company is profitable.
Pros and cons of acquisitions
There are several pros and cons to acquisitions:
Pros of acquisitions
- On the plus side, acquisitions can help a company grow quickly and gain market share. They can also bring new technology and expertise into the company.
- Acquisitions can help to improve the company’s financial position by providing a new source of revenue or reducing costs.
Cons of acquisitions
- One key downside is that acquisitions can be very costly in terms of the initial purchase price and the ongoing costs of integrating the acquired company into the existing business. This can lead to financial strain and debt if the acquisition is not properly managed.
- Additionally, there is always the risk that the acquired company will not mesh well with the existing business, leading to operational problems and inefficiencies.
- Finally, there is the potential for a cultural clash between the employees of the two companies, which can create tension and discord.
Purpose of an acquisition
The purpose of acquisitions is to secure new resources and capabilities to help the company grow. This can be done by buying another company, investing in new technology, or acquiring new patents or other intellectual property. The key is to find something that will complement the company’s existing strengths and help it move into new markets or expand its reach.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are corporate transactions involving the combining of two companies. A merger occurs when two companies combine to form a new company, while an acquisition occurs when one company buys another.
There are several key differences between mergers and acquisitions.
- Both companies must agree to combine in a merger, whereas only one company must agree to be acquired in an acquisition.
- In a merger, the two companies combine to form a new company. In contrast, in an acquisition, the acquiring company buys the other company and absorbs it into its existing business.
- Finally, mergers tend to be more complex and time-consuming than acquisitions, as they involve the creation of a new company.
The step-by-step acquisition process involves four main stages: prospecting, screening, due diligence, and closing.
- Prospecting is the first stage and involves identifying potential targets that fit the buyer’s criteria.
- Once potential targets are identified, the buyer will screen them to assess whether they are suitable acquisition candidates.
- The due diligence stage is the next step and involves the buyer conducting a thorough investigation of the target company. This stage is important to identify potential risks or problems arising from the acquisition.
- Once due diligence is complete, the buyer will negotiate with the target company to agree on a purchase price.
- Once a purchase price is agreed upon, the buyer will complete the acquisition by acquiring all the necessary financing and legal approvals.
When a company with strong financial standing purchases shares worth more than 50% of an entity with weaker financial standing, an acquisition occurs then.
The Latin verb acqurere, which means “to increase one’s assets,” is where the word “acquisition” ultimately derives from. The term “acquisition” is most frequently used in the realm of business to describe buying a business or piece of real estate or taking ownership of something.
Evaluating acquisition candidates is assessing potential target companies to determine whether or not they would be a good fit for your company.
This involves looking at various factors, including the target company’s financials, its strategic fit with your company, and the cultural fit between the two organisations.
The goal is to identify companies that would be a good fit for your company in terms of its long-term goals and objectives.
Related Terms
- Trailing Stops
- Exchange Control
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Hyperdeflation
- Hope Credit
- Futures contracts
- Human capital
- Subrogation
- Qualifying Annuity
- Strategic Alliance
- Probate Court
- Procurement
- Holding company
- Harmonic mean
- Trailing Stops
- Exchange Control
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Hyperdeflation
- Hope Credit
- Futures contracts
- Human capital
- Subrogation
- Qualifying Annuity
- Strategic Alliance
- Probate Court
- Procurement
- Holding company
- Harmonic mean
- Income protection insurance
- Recession
- Savings Ratios
- Pump and dump
- Total Debt Servicing Ratio
- Debt to Asset Ratio
- Liquid Assets to Net Worth Ratio
- Liquidity Ratio
- Personal financial ratios
- T-bills
- Payroll deduction plan
- Operating expenses
- Demand elasticity
- Deferred compensation
- Conflict theory
- Acid-test ratio
- Withholding Tax
- Benchmark index
- Double Taxation Relief
- Debtor Risk
- Securitization
- Yield on Distribution
- Currency Swap
- Overcollateralization
- Efficient Frontier
- Listing Rules
- Green Shoe Options
- Accrued Interest
- Market Order
- Accrued Expenses
- Target Leverage Ratio
- Acceptance Credit
- Balloon Interest
- Abridged Prospectus
- Data Tagging
- Perpetuity
- Hybrid annuity
- Investor fallout
- Intermediated market
- Information-less trades
- Back Months
- Adjusted Futures Price
- Expected maturity date
- Excess spread
- Quantitative tightening
- Accreted Value
- Equity Clawback
- Soft Dollar Broker
- Stagnation
- Replenishment
- Decoupling
- Holding period
- Regression analysis
- Wealth manager
- Financial plan
- Adequacy of coverage
- Actual market
- Credit risk
- Insurance
- Financial independence
- Annual report
- Financial management
- Ageing schedule
- Global indices
- Folio number
- Accrual basis
- Liquidity risk
- Quick Ratio
- Unearned Income
- Sustainability
- Value at Risk
- Vertical Financial Analysis
- Residual maturity
- Operating Margin
- Trust deed
- Leverage
- Profit and Loss Statement
- Junior Market
- Affinity fraud
- Base currency
- Working capital
- Individual Savings Account
- Redemption yield
- Net profit margin
- Fringe benefits
- Fiscal policy
- Escrow
- Externality
- Multi-level marketing
- Joint tenancy
- Liquidity coverage ratio
- Hurdle rate
- Kiddie tax
- Giffen Goods
- Keynesian economics
- EBITA
- Risk Tolerance
- Disbursement
- Bayes’ Theorem
- Amalgamation
- Adverse selection
- Contribution Margin
- Accounting Equation
- Value chain
- Gross Income
- Net present value
- Liability
- Leverage ratio
- Inventory turnover
- Gross margin
- Collateral
- Being Bearish
- Being Bullish
- Commodity
- Exchange rate
- Basis point
- Inception date
- Riskometer
- Trigger Option
- Zeta model
- Racketeering
- Market Indexes
- Short Selling
- Quartile rank
- Defeasance
- Cut-off-time
- Business-to-Consumer
- Bankruptcy
- Turnover Ratio
- Indexation
- Fiduciary responsibility
- Benchmark
- Pegging
- Illiquidity
- Backwardation
- Backup Withholding
- Buyout
- Beneficial owner
- Contingent deferred sales charge
- Exchange privilege
- Asset allocation
- Maturity distribution
- Letter of Intent
- Emerging Markets
- Consensus Estimate
- Cash Settlement
- Cash Flow
- Capital Lease Obligations
- Book-to-Bill-Ratio
- Capital Gains or Losses
- Balance Sheet
- Capital Lease
Most Popular Terms
Other Terms
- Physical ETF
- Initial Public Offering
- Buyback
- Secondary Sharing
- Bookrunner
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Payment Date
- Secondary Market
- Margin Requirement
- Mark-to-market
- Pledged Asset
- Yield Pickup
- Subordinated Debt
- Treasury Stock Method
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Bullet Bonds
- Basket Trade
- Contrarian Strategy
- Notional Value
- Speculation
- Stub
- Trading Volume
- Going Long
- Pink sheet stocks
- Rand cost averaging
- Sustainable investment
- Stop-limit sell order
- Economic Bubble
- Ask Price
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Stock symbol
- Companion tranche
- Synthetic replication
- Bourse
- Beneficiary
- Witching Hour
- Widow and Orphan stock
- Public Float
- Closing Price
- Reverse stock splits
- Quiet period
- Prepayment risk
Know More about
Tools/Educational Resources
Markets Offered by POEMS
Read the Latest Market Journal

Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Start trading on POEMS! Open a free account here! At a glance: Major indices continue...

Weekly Updates 15/4/24 – 19/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
In recent years, inflation has become a hot topic, evoking strong emotions as the cost...

Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
Source: eSignal, Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. In the heart of Japan’s economic landscape, the Nikkei 225...

Weekly Updates 8/4/24 – 12/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and...

What Makes Forex Trading Attractive?
In a world where the click of a button can send goods across oceans and...

Weekly Updates 1/4/24 – 5/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

How to soar higher with Positive Carry!
As US Fed interest rates are predicted to rise 6 times this year, it’s best...












