Trust deed
Table of Contents
Trust deed
The amount of paperwork needed to apply for a mortgage may seem endless. One of the papers that may be crucial for the closing of your house deal is a trust deed. Knowing what a trust deed is and how it works might be useful if you’re trying to buy a new home. A trust deed is an agreement between a lender and borrower to give ownership of the property to a neutral third party who will hold it until the loan is repaid.
What is a trust deed?
A trust deed, often called a deed of trust, is a legal document signed when a property is purchased. In secured real estate transactions, it is used in some states instead of a mortgage. This agreement outlines how the loan will be repaid and is made between the property buyer and the lender. Until the loan is fully returned, a third person, known as a trustee, keeps the legal title to the property.
Understanding trust deeds
In some states, trust deeds serve as an alternative to mortgages. A trust deed transfers property ownership to a third party or trustee rather than directly between a lender and a borrower. The property is entirely transferred to the borrower once the borrower has fulfilled the debt conditions to the lender.
The trustor, trustee, and beneficiary are the three crucial persons in a property trust deed. The person who buys the property and becomes the trustor. Their property is in the trust and will be kept there until the loan has been paid off in full. Although not holding the property’s legal title, the trustor will be its owner and have all its rights.
The trustee is the party in charge of keeping title to the trust’s assets. Once the loan payment has been made in full, they must formally transfer the title. The lender who assists in financing the transaction is the beneficiary. In rare circumstances, the trustee may also be the beneficiary.
What is included in a trust deed?
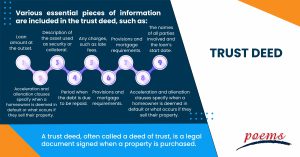
Various essential pieces of information are included in the trust deed, such as:
- Loan amount at the outset.
- Description of the asset used as security or collateral.
- The names of all parties involved and the loan’s start date.
- Period when the debt is due to be repaid.
- Any charges, such as late fees.
- Provisions and mortgage requirements.
- Legal processes, such as a power of sale clause, in the event of default.
- Acceleration and alienation clauses specify when a homeowner is deemed in default or what occurs if they sell their property.
- Any add-ons that contain stipulations like adjustable-rate mortgage terms or prepayment penalties.
Pros and cons of investing in trust deeds
There are various pros to investing in the trust deed. The typical security for trust deed investments are real estate, which you can touch and own if the loan defaults and you are forced to foreclose. Trust deed investments are, therefore, more secure than other, higher-risk investments. Real estate is a relatively safe investment if it maintains its value.
Additionally, if you have to foreclose, you can sell the property and return your investment. Investing in trust deeds typically produces a good rate of return. The rate will vary depending on the property, the contract, and the parties, but you may expect an average return of 8% to 12%. Lending to a borrower with a successful track record can lower risk, though it is not guaranteed.
There are also various limitations and cons of investing in trust deeds. As FDIC insurance does not cover trust deeds, there is no assurance that your money will be returned in full. Partnering with a successful broker can help you achieve success. They can advise you on handling your trust deed investments best.
Working with a borrower directly, whose interests can be at odds with yours, is not a good idea. It is preferable to work with an impartial broker who can help coordinate a win-win situation for everyone. Trust deeds have their peculiarities and risks, much like any investment, whether a mortgage note investment or a trust deed investment. Having a knowledgeable, accredited broker at your side never hurts.
Example of a trust deed
Consider the following real estate trust deed example to understand the idea further. Beth wants to purchase a home. She resides in Brooklyn and wants to use a trust deed to finance the house.
The bank granted the loan and informed her that the house would be held in trust, with ABC as the trustee until the debt was paid off. She is aware of additional information regarding interest, other proceedings, and the loan’s 20-year term. By signing it, Beth completed the agreement with ABC and her bank.
Frequently Asked Questions
Assignment of a trust deed in real estate law is simply the transfer of a trust deed from one party to another, typically when the beneficiary sells their loan to another lender. With the use of this deed of assignment, the present owner of a life insurance policy may transfer ownership to another individual or company.
Reconveyance in a Deed of Trust is a document that the mortgage holder issues to show that the borrower has been discharged from his mortgage debt and to assist in transferring ownership of the property from the beneficiary to the borrower.
Trust deeds entail a quicker, less expensive non-judicial foreclosure of the loan. A mortgage necessitates judicial foreclosure of the debt, which is costly and time-consuming.
In a deed of trust, the trustee must be a lawyer, title insurance company, trust firm, bank, savings and loan, credit union, or other business specifically permitted by law to act in that capacity.
A power of sale clause in a mortgage note gives the mortgagee the right to sell the property in the event of default so that the mortgage obligation is paid off. A trustee’s sale is one of the options available to a lender if you fall behind on your mortgage payments.
Related Terms
- Trailing Stops
- Exchange Control
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Hyperdeflation
- Hope Credit
- Futures contracts
- Human capital
- Subrogation
- Qualifying Annuity
- Strategic Alliance
- Probate Court
- Procurement
- Holding company
- Harmonic mean
- Trailing Stops
- Exchange Control
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Hyperdeflation
- Hope Credit
- Futures contracts
- Human capital
- Subrogation
- Qualifying Annuity
- Strategic Alliance
- Probate Court
- Procurement
- Holding company
- Harmonic mean
- Income protection insurance
- Recession
- Savings Ratios
- Pump and dump
- Total Debt Servicing Ratio
- Debt to Asset Ratio
- Liquid Assets to Net Worth Ratio
- Liquidity Ratio
- Personal financial ratios
- T-bills
- Payroll deduction plan
- Operating expenses
- Demand elasticity
- Deferred compensation
- Conflict theory
- Acid-test ratio
- Withholding Tax
- Benchmark index
- Double Taxation Relief
- Debtor Risk
- Securitization
- Yield on Distribution
- Currency Swap
- Overcollateralization
- Efficient Frontier
- Listing Rules
- Green Shoe Options
- Accrued Interest
- Market Order
- Accrued Expenses
- Target Leverage Ratio
- Acceptance Credit
- Balloon Interest
- Abridged Prospectus
- Data Tagging
- Perpetuity
- Hybrid annuity
- Investor fallout
- Intermediated market
- Information-less trades
- Back Months
- Adjusted Futures Price
- Expected maturity date
- Excess spread
- Quantitative tightening
- Accreted Value
- Equity Clawback
- Soft Dollar Broker
- Stagnation
- Replenishment
- Decoupling
- Holding period
- Regression analysis
- Wealth manager
- Financial plan
- Adequacy of coverage
- Actual market
- Credit risk
- Insurance
- Financial independence
- Annual report
- Financial management
- Ageing schedule
- Global indices
- Folio number
- Accrual basis
- Liquidity risk
- Quick Ratio
- Unearned Income
- Sustainability
- Value at Risk
- Vertical Financial Analysis
- Residual maturity
- Operating Margin
- Leverage
- Profit and Loss Statement
- Junior Market
- Affinity fraud
- Base currency
- Working capital
- Individual Savings Account
- Redemption yield
- Net profit margin
- Fringe benefits
- Fiscal policy
- Escrow
- Externality
- Multi-level marketing
- Joint tenancy
- Liquidity coverage ratio
- Hurdle rate
- Kiddie tax
- Giffen Goods
- Keynesian economics
- EBITA
- Risk Tolerance
- Disbursement
- Bayes’ Theorem
- Amalgamation
- Adverse selection
- Contribution Margin
- Accounting Equation
- Value chain
- Gross Income
- Net present value
- Liability
- Leverage ratio
- Inventory turnover
- Gross margin
- Collateral
- Being Bearish
- Being Bullish
- Commodity
- Exchange rate
- Basis point
- Inception date
- Riskometer
- Trigger Option
- Zeta model
- Racketeering
- Market Indexes
- Short Selling
- Quartile rank
- Defeasance
- Cut-off-time
- Business-to-Consumer
- Bankruptcy
- Acquisition
- Turnover Ratio
- Indexation
- Fiduciary responsibility
- Benchmark
- Pegging
- Illiquidity
- Backwardation
- Backup Withholding
- Buyout
- Beneficial owner
- Contingent deferred sales charge
- Exchange privilege
- Asset allocation
- Maturity distribution
- Letter of Intent
- Emerging Markets
- Consensus Estimate
- Cash Settlement
- Cash Flow
- Capital Lease Obligations
- Book-to-Bill-Ratio
- Capital Gains or Losses
- Balance Sheet
- Capital Lease
Most Popular Terms
Other Terms
- Physical ETF
- Initial Public Offering
- Buyback
- Secondary Sharing
- Bookrunner
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Payment Date
- Secondary Market
- Margin Requirement
- Mark-to-market
- Pledged Asset
- Yield Pickup
- Subordinated Debt
- Treasury Stock Method
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Bullet Bonds
- Basket Trade
- Contrarian Strategy
- Notional Value
- Speculation
- Stub
- Trading Volume
- Going Long
- Pink sheet stocks
- Rand cost averaging
- Sustainable investment
- Stop-limit sell order
- Economic Bubble
- Ask Price
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Stock symbol
- Companion tranche
- Synthetic replication
- Bourse
- Beneficiary
- Witching Hour
- Widow and Orphan stock
- Public Float
- Closing Price
- Reverse stock splits
- Quiet period
- Prepayment risk
Know More about
Tools/Educational Resources
Markets Offered by POEMS
Read the Latest Market Journal

Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Start trading on POEMS! Open a free account here! At a glance: Major indices continue...

Weekly Updates 15/4/24 – 19/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
In recent years, inflation has become a hot topic, evoking strong emotions as the cost...

Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
Source: eSignal, Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. In the heart of Japan’s economic landscape, the Nikkei 225...

Weekly Updates 8/4/24 – 12/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and...

What Makes Forex Trading Attractive?
In a world where the click of a button can send goods across oceans and...

Weekly Updates 1/4/24 – 5/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

How to soar higher with Positive Carry!
As US Fed interest rates are predicted to rise 6 times this year, it’s best...


















