Cryptocurrency
Table of Contents
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are a new and exciting technology with the potential to change the financial system as we know it. Nevertheless, there remains a lot of uncertainty regarding how they will be utilised in the future.
What is cryptocurrency?
A digital or virtual money that employs cryptography for security is called cryptocurrency. The term “crypto” refers to the numerous cryptographic methods that protect these entries, such as hashing, public-private key pairings, and elliptical curve encryption.
Since cryptocurrencies are decentralised, neither a government nor a financial institution can control them. The earliest and best-known cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, was developed in 2009. On decentralised exchanges, cryptocurrency is often exchanged and may be used to make purchases of products and services.
Understanding cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are powered by blockchain technology. Cryptocurrencies are powered by blockchain technology. Blockchain is a digital ledger of all of the cryptocurrency transactions. Blockchain technology is used to secure and track transactions. Bitcoin, for example, uses a blockchain to track and verify all transactions on the Bitcoin network.
Popular cryptocurrencies include litecoin, bitcoin, monero and ether. Cryptographic methods, which are maintained and verified through a process called mining, a network of computers or specialised hardware, such as application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), process and validate the transactions, and cryptocurrencies are generated (and secured). The procedure rewards the miners who power the Bitcoin network.
Cryptocurrency assets are often volatile, meaning their prices can fluctuate dramatically. This volatility can make cryptocurrencies a risky investment. However, some believe the volatility will decrease as the market matures.
Types of cryptocurrency
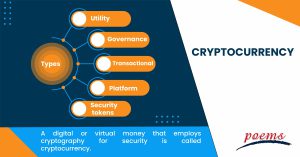
Knowing the different kinds of cryptocurrencies is important, as so many are available nowadays. Knowing if the coin you’re considering serves a purpose will help you evaluate whether investing in it is worthwhile; a cryptocurrency without a use case is riskier than one with one.
Typically, the coin’s name is included while discussing different cryptocurrency varieties. But coin kinds and coin names are different. The following are some of the categories of tokens you could encounter, along with their names:
- Utility
Tokens with this feature include XRP and ETH. On their blockchains, they perform certain roles.
- Governance
These tokens on a blockchain like Uniswap reflect voting or other privileges.
- Transactional
Tokens made to be used as a form of payment. Of these, Bitcoin is the most well-known.
- Platform
These tokens serve programs designed to work with a blockchain like Solana.
- Security tokens
Tokens that reflect ownership of an asset, such as a tokenized stock, are known as security tokens (value transferred to the blockchain). A securitized token is the MS Token, for instance. The Millennium Sapphire may be partially acquired if you can locate one for sale.
Cryptocurrency – how it is produced
Blockchain, a decentralised public ledger updated and maintained by currency holders, is the technology that underlies cryptocurrencies.
The process of “mining,” employing computers’ power to solve challenging mathematical problems to produce coins, is how cryptocurrency units are produced. Additionally, users may purchase the currency from brokers, keep them in encrypted wallets, and then use them to make purchases.
Cryptocurrency ownership entails the lack of any material possessions. What you hold is a key that permits you to move information or a unit of measurement from one person to another without the aid of a trustworthy third party.
Examples cryptocurrency
Examples of cryptocurrencies include:
- Bitcoin
Bitcoin, the first and most prominent cryptocurrency, was created in 2009. The currency’s creator is commonly thought to be Satoshi Nakamoto, an alias for a person or team whose exact identity is still unknown.
- Ethereum
Ethereum, another popular cryptocurrency, was created in 2015. Ethereum differs from Bitcoin in that it allows for smart contracts or contracts that can be executed automatically according to certain conditions.
- Litecoin
Litecoin, another popular cryptocurrency, was created in 2011. In many aspects, Litecoin and Bitcoin are similar, but it is designed to be faster and cheaper to transact.
- Bitcoin cash
It is a fork of Bitcoin, created in 2017. Bitcoin Cash is similar to Bitcoin but has a larger block size, meaning it can process more transactions per second.
Frequently Asked Questions
Generally, use these easy steps to purchase cryptocurrency:
- Select a broker or cryptocurrency exchange
- Register for an account and verify it
- Deposit money to invest
- Place your order for cryptocurrency
- Pick a storage approach
You may purchase cryptocurrencies using alternative methods, such as:
It is important to consider if the popularity that cryptocurrencies have achieved over time is real. Cryptocurrency, particularly Bitcoin, has, even though it is still far from replacing institutionalised cash, gained widespread acceptability worldwide.
They can be used as a mode of payment. Bitcoin was initially of limited value as a method of payment to retailers. But over time, many businesses, including eateries, airlines, jewellers, and apps, have begun to recognise it as a legitimate form of payment.
Additionally, cryptocurrencies, particularly Bitcoin, are among the most profitable investment opportunities available. Its value growth is dynamic and may be a great route for capital growth.
The price of cryptocurrencies is highly volatile and can change rapidly. Governments or financial institutions do not regulate cryptocurrencies, so their value is determined by supply and demand on the open market. The price of a cryptocurrency is also influenced by factors such as media coverage, public interest, and even rumours.
Bitcoins are kept in a digital wallet, just like we store credit cards or cash in a physical wallet. Digital wallets can be web-based or hardware-based. The wallet can be stored on a desktop computer or mobile device or kept secure by writing the private keys and access addresses on paper.
Some of the safest methods to keep cryptocurrency are in custodial and hardware wallets, but each has benefits and limitations.
For certain companies, the use of cryptocurrencies may present opportunities. The advantages might include the following:
- A crypto transaction often happens quickly. For instance, only a computer or smartphone is required to move Bitcoins from one digital wallet to another.
- Cheaper and quicker money transactions and decentralised networks that do not have a sole point of failure are two benefits of cryptocurrencies.
- Blockchain seeks to eliminate middlemen like banks and internet marketplaces, so there are no transaction costs.
- Payments made using cryptocurrencies are becoming more common among big businesses and industries like fashion and medicine.
Cryptocurrencies’ drawbacks include their unstable prices, high energy requirements for mining, and usage in illegal activities. Additionally, cyber attacks often target cryptocurrency exchanges, which might mean that you permanently lose your investments.
Related Terms
- International securities exchanges
- Margin Requirement
- Pledged Asset
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Prepayment risk
- Homemade leverage
- Prime bank investments
- ESG
- Capitulation
- Shareholder service fees
- Insurable Interest
- Minority Interest
- Passive Investing
- Market cycle
- Progressive tax
- International securities exchanges
- Margin Requirement
- Pledged Asset
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Prepayment risk
- Homemade leverage
- Prime bank investments
- ESG
- Capitulation
- Shareholder service fees
- Insurable Interest
- Minority Interest
- Passive Investing
- Market cycle
- Progressive tax
- Correlation
- NFT
- Carbon credits
- Hyperinflation
- Hostile takeover
- Travel insurance
- Money market
- Dividend investing
- Digital Assets
- Coupon yield
- Counterparty
- Sharpe ratio
- Alpha and beta
- Investment advisory
- Wealth management
- Variable annuity
- Asset management
- Value of Land
- Investment Policy
- Investment Horizon
- Forward Contracts
- Equity Hedging
- Encumbrance
- Money Market Instruments
- Share Market
- Opening price
- Transfer of Shares
- Alternative investments
- Lumpsum
- Derivatives market
- Operating assets
- Hypothecation
- Accumulated dividend
- Assets under management
- Endowment
- Return on investment
- Investments
- Acceleration clause
- Heat maps
- Lock-in period
- Tranches
- Stock Keeping Unit
- Real Estate Investment Trusts
- Prospectus
- Turnover
- Tangible assets
- Preference Shares
- Open-ended investment company
- Standard deviation
- Independent financial adviser
- ESG investing
- Earnest Money
- Primary market
- Leveraged Loan
- Transferring assets
- Shares
- Fixed annuity
- Underlying asset
- Quick asset
- Portfolio
- Mutual fund
- Xenocurrency
- Bitcoin Mining
- Option contract
- Depreciation
- Inflation
- Options
- Asset
- Reinvestment option
- Capital appreciation
- Style Box
- Top-down Investing
- Trail commission
- Unit holder
- Yield curve
- Rebalancing
- Vesting
- Private equity
- Bull Market
- Absolute Return
- Leaseback
- Impact investing
- Venture Capital
- Buy limit
- Asset stripper
- Volatility
- Investment objective
- Annuity
- Sustainable investing
- Face-amount certificate
- Lipper ratings
- Investment stewardship
- Average accounting return
- Asset class
- Active management
- Breakpoint
- Expense ratio
- Bear market
- Annualised rate of return
- Hedging
- Equity options
- Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA)
- Due Diligence
- Contrarian Investor
Most Popular Terms
Other Terms
- Settlement currency
- Federal funds rate
- Active Tranche
- Convertible Securities
- Synthetic ETF
- Physical ETF
- Initial Public Offering
- Buyback
- Secondary Sharing
- Bookrunner
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Payment Date
- Secondary Market
- Mark-to-market
- Yield Pickup
- Subordinated Debt
- Trailing Stops
- Treasury Stock Method
- Bullet Bonds
- Basket Trade
- Contrarian Strategy
- Exchange Control
- Notional Value
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Speculation
- Stub
- Trading Volume
- Going Long
- Pink sheet stocks
- Rand cost averaging
- Sustainable investment
- Stop-limit sell order
- Economic Bubble
- Ask Price
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Stock symbol
- Companion tranche
- Synthetic replication
- Bourse
- Beneficiary
- Witching Hour
Know More about
Tools/Educational Resources
Markets Offered by POEMS
Read the Latest Market Journal

Predicting Trend Reversals with Candlestick Patterns for Beginners
Candlestick patterns are used to predict the future direction of price movements as they contain...

In the diverse and complex world of investing, unit trusts stand out as a popular...

Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Start trading on POEMS! Open a free account here! At a glance: Major indices continue...

Weekly Updates 15/4/24 – 19/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
In recent years, inflation has become a hot topic, evoking strong emotions as the cost...

Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
Source: eSignal, Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. In the heart of Japan’s economic landscape, the Nikkei 225...

Weekly Updates 8/4/24 – 12/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and...

What Makes Forex Trading Attractive?
In a world where the click of a button can send goods across oceans and...