Top-down Investing
Table of Contents
Top-down Investing
Making judgments based on the status of the economy and multiple marketplaces is a top-down approach. A top-down investor may begin with a broad, bird’s-eye view that covers important aspects. A top-down investor focuses on broad causes and topics such as national and global developments, also referred to as macro or macroeconomic strategy.
What is top-down investing?
Top-down investing is a technique or strategy that, like a funnel, starts with a broad view of the market and then narrows it until you can make an investment choice.
The first step in a top-down study is to examine the overall situation or the relevant macroeconomic elements. Investors can therefore start by researching the GDP, inflation rates, and rise and fall of interest rates of the country in question before determining whether or not to invest.
Investors will use the information gathered once this analysis is finished to forecast how a stock market will behave over the coming days. Finally, based on this forecast, they will determine whether the stock of a specific company has the potential to generate significant profits.
Understanding top-down investing
A top-down strategy is simply an EIC approach to investing. E stands for economy, and you decide first whether the current state of the national and international economies is favorable for investment.
Once the economic requirement is met, you evaluate “I,” which stands for the company’s industry. You consider the industry’s rate of expansion, input prices, output price patterns, and industry entry obstacles, among other things.
You proceed to the last step once the investor is convinced that the industry’s advantages and possibilities outweigh its dangers and disadvantages. C stands for the particular business you plan to invest in and which has passed the Economy and Industry test.
You then dig into the numbers, such as profitability, solvency, liquidity, efficiency, valuations, etc. The top-down strategy is put into practice based on this EIC methodology.
Order of analysis in top-down investing
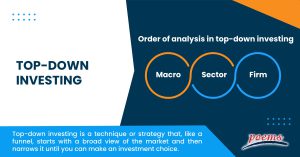
The top-down strategy depends on thoroughly examining numerous economic aspects in the following order.
- Macro
These economic parameters include things like GDP, inflation, and more.
- Sector
Investors focus their research in this second stage of analysis solely on the industry in which they wish to invest. Therefore, a person intending to invest in a car firm would assess the current market performance of the automotive industry as a whole, identifying potential opportunities or difficulties the industry may encounter in the future.
- Firm
Assessing the potential of a certain business or company whose stocks an investor wants to buy is the final step in top-down investing.
Salient benefits of top-down investments
The following are the various salient benefits of top-down investments:
- This approach guarantees that investors are aware of the best asset for maximizing gains, independent of the market situation and the state of the economy.
- Investors will be better able to identify a declining market if they consider the macro issues. Even if they meet every other requirement, it will restrict them from making stock investments.
- A top-down investment strategy also reveals situations where a sizable investment would not be suitable for a portfolio of investors. It stops them from making excessive investments.
- Investments from the top down also promote diversification. Such a strategy compels people to think about the best international markets and spread their investments throughout the top industries.
Drawbacks of top-down investments
The top-down technique has several drawbacks, too, some of which are listed below:
- The approach could make an investor overlook crucial differences between investments and businesses. Not every business succeeds, for instance, when some industries are booming.
- Markets can be unpredictable. Although indicators may suggest a particular result, this isn’t necessarily the case.
- More study of the subject is necessary. Many complex macro factors are always changing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Top-down investing considers macroeconomic aspects when making investment decisions. In contrast, bottom-up investing considers business-specific elements such as financials, demand, and supply, as well as the types of goods and services a corporation supplies.
Top-down investing starts with selecting assets at the macroeconomic scale, looking first at global markets, then industries and sectors, and lastly, individual enterprises.
Before investigating microeconomic elements like particular industries or companies, top-down investing focuses on the macroeconomic factors of the economy, such as the GDP.
Bottom-up investing emphasizes individual company performance and fundamentals before considering macro considerations.
If a nation or region’s economy is strong, top-down investors may decide to invest there. So, an investor might buy equities, mutual funds, or exchange-traded funds if the European economy is doing well, for instance.
An example of top-down investing would be if an investor were to first look at the overall economy and make investment decisions based on that. For instance, if the economy were doing well, the investor might put money into stocks, but if the economy were doing poorly, the investor might put money into bonds. This type of investing is based on the idea that the economy drives the stock market.
Top-down investing is an investment research approach concentrating on macroeconomic issues such as GDP, taxation, employment, interest rates, and so on before studying microeconomic aspects such as individual industries or enterprises.
Some of the benefits of top-down investing are:
- You become a more knowledgeable investor as you study more about economic plans and indicators.
- Top-down investment does not require a thorough understanding of financial markets or the stock market.
- The method assists you in identifying opportunities in sectors and places you would not have investigated otherwise.
The top-down approach also has certain drawbacks:
- The strategy may lead investors to overlook key differences between businesses and investments. When some industries, for example, grow, not every business succeeds.
- The market is not always predictable. Although indicators might indicate a given conclusion, this is not always the case.
- More study is needed in this area. The macro factors are many, intricate, and constantly changing.
Related Terms
- Margin Requirement
- Pledged Asset
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Prepayment risk
- Homemade leverage
- Prime bank investments
- ESG
- Capitulation
- Shareholder service fees
- Insurable Interest
- Minority Interest
- Passive Investing
- Market cycle
- Progressive tax
- Correlation
- Margin Requirement
- Pledged Asset
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Prepayment risk
- Homemade leverage
- Prime bank investments
- ESG
- Capitulation
- Shareholder service fees
- Insurable Interest
- Minority Interest
- Passive Investing
- Market cycle
- Progressive tax
- Correlation
- NFT
- Carbon credits
- Hyperinflation
- Hostile takeover
- Travel insurance
- Money market
- Dividend investing
- Digital Assets
- Coupon yield
- Counterparty
- Sharpe ratio
- Alpha and beta
- Investment advisory
- Wealth management
- Variable annuity
- Asset management
- Value of Land
- Investment Policy
- Investment Horizon
- Forward Contracts
- Equity Hedging
- Encumbrance
- Money Market Instruments
- Share Market
- Opening price
- Transfer of Shares
- Alternative investments
- Lumpsum
- Derivatives market
- Operating assets
- Hypothecation
- Accumulated dividend
- Assets under management
- Endowment
- Return on investment
- Investments
- Acceleration clause
- Heat maps
- Lock-in period
- Tranches
- Stock Keeping Unit
- Real Estate Investment Trusts
- Prospectus
- Turnover
- Tangible assets
- Preference Shares
- Open-ended investment company
- Standard deviation
- Independent financial adviser
- ESG investing
- Earnest Money
- Primary market
- Leveraged Loan
- Transferring assets
- Shares
- Fixed annuity
- Underlying asset
- Quick asset
- Portfolio
- Mutual fund
- Xenocurrency
- Bitcoin Mining
- Option contract
- Depreciation
- Inflation
- Cryptocurrency
- Options
- Asset
- Reinvestment option
- Capital appreciation
- Style Box
- Trail commission
- Unit holder
- Yield curve
- Rebalancing
- Vesting
- Private equity
- Bull Market
- Absolute Return
- Leaseback
- Impact investing
- Venture Capital
- Buy limit
- Asset stripper
- Volatility
- Investment objective
- Annuity
- Sustainable investing
- Face-amount certificate
- Lipper ratings
- Investment stewardship
- Average accounting return
- Asset class
- Active management
- Breakpoint
- Expense ratio
- Bear market
- Annualised rate of return
- Hedging
- Equity options
- Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA)
- Due Diligence
- Contrarian Investor
Most Popular Terms
Other Terms
- Physical ETF
- Initial Public Offering
- Buyback
- Secondary Sharing
- Bookrunner
- Notional amount
- Negative convexity
- Jumbo pools
- Inverse floater
- Forward Swap
- Underwriting risk
- Reinvestment risk
- Final Maturity Date
- Payment Date
- Secondary Market
- Mark-to-market
- Yield Pickup
- Subordinated Debt
- Trailing Stops
- Treasury Stock Method
- Bullet Bonds
- Basket Trade
- Contrarian Strategy
- Exchange Control
- Notional Value
- Relevant Cost
- Dow Theory
- Speculation
- Stub
- Trading Volume
- Going Long
- Pink sheet stocks
- Rand cost averaging
- Sustainable investment
- Stop-limit sell order
- Economic Bubble
- Ask Price
- Constant prepayment rate
- Covenants
- Stock symbol
- Companion tranche
- Synthetic replication
- Bourse
- Beneficiary
- Witching Hour
- Widow and Orphan stock
- Public Float
- Closing Price
- Reverse stock splits
- Quiet period
Know More about
Tools/Educational Resources
Markets Offered by POEMS
Read the Latest Market Journal

Back in Business: The Return of IPOs & Top Traded Counters in March 2024
Start trading on POEMS! Open a free account here! At a glance: Major indices continue...

Weekly Updates 15/4/24 – 19/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

From $50 to $100: Unveiling the Impact of Inflation
In recent years, inflation has become a hot topic, evoking strong emotions as the cost...

Japan’s Economic Resurgence: Unveiling the Tailwinds Behind Nikkei 225’s Record Leap
Source: eSignal, Intercontinental Exchange, Inc. In the heart of Japan’s economic landscape, the Nikkei 225...

Weekly Updates 8/4/24 – 12/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and...

What Makes Forex Trading Attractive?
In a world where the click of a button can send goods across oceans and...

Weekly Updates 1/4/24 – 5/4/24
This weekly update is designed to help you stay informed and relate economic and company...

How to soar higher with Positive Carry!
As US Fed interest rates are predicted to rise 6 times this year, it’s best...












